Feb 16, 2022 (Nanowerk News) Scientists in Japan have made a tuneable, elastic and temperature-sensitive gel by using complementary DNA strands to connect star-shaped polymer molecules together. The gel, and the method used to develop it, could lead to advances in tissue regeneration, drug delivery and soft robotics. Xiang Li...
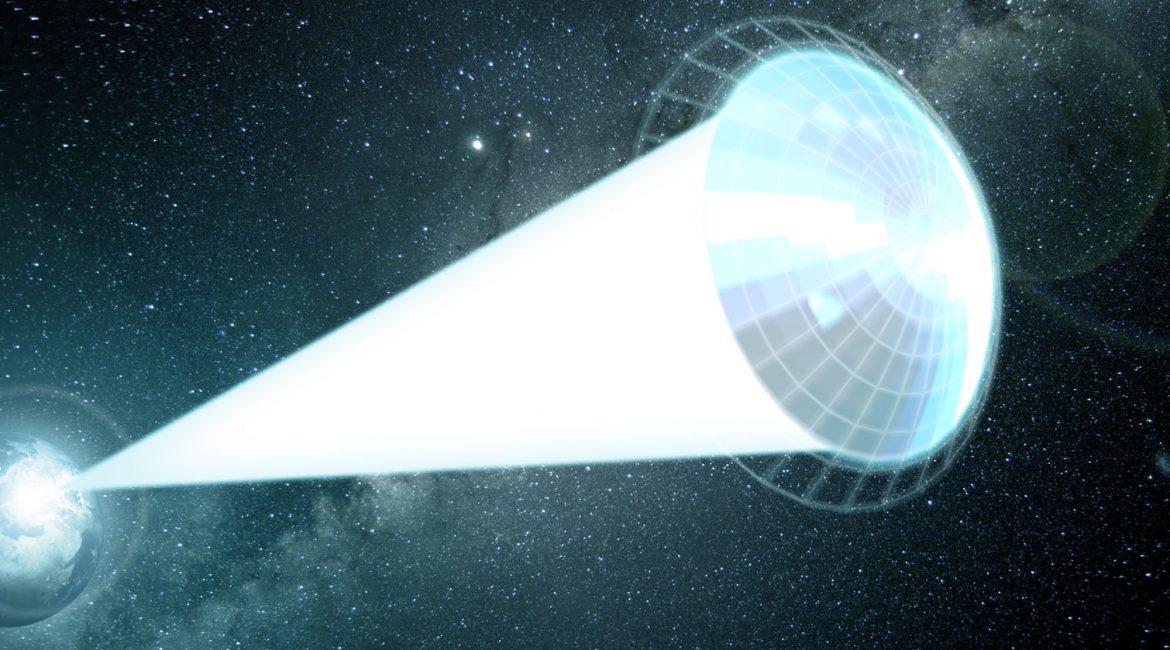
How to design a lightsail that won’t tear or melt on an interstellar voyage
Feb 16, 2022 (Nanowerk News) Astronomers have been waiting decades for the launch of the James Webb Space Telescope, which promises to peer farther into space than ever before. But if humans want to actually reach our nearest stellar neighbor, they will need to wait quite a bit longer: a...
Supermassive black hole caught hiding in a ring of cosmic dust
Feb 16, 2022 (Nanowerk News) Active Galactic Nuclei (AGNs) are extremely energetic sources powered by supermassive black holes and found at the centre of certain galaxies. These black holes are fed by large volumes of cosmic dust and gas. This material spirals towards the black hole and huge amounts of...
A novel nanoplatform for delivering drugs into lymphocytes
Feb 16, 2022 (Nanowerk News) T cells, also known as lymphocytes, have important roles in various immune reactions. However, there are only a few reports on delivery systems into T cells. Realizing this, it is essential to work and actively contribute in controlling immune systems. Associate Professor Chie Kojima and...
What’s inside a black hole? A physicist uses quantum computing, machine learning to find out
Feb 16, 2022 (Nanowerk News) Dude, what if everything around us was just … a hologram? The thing is, it could be—and a University of Michigan physicist is using quantum computing and machine learning to better understand the idea, called holographic duality. Holographic duality is a mathematical conjecture that connects...
Using graphene oxide to rebuild bone tissue
Feb 16, 2022 (Nanowerk News) Over the last 30 years, the scientific community has been working to develop a synthetic alternative to bone grafts for repairing diseased or damaged bone. McGill University researchers used the Canadian Light Source (CLS) at the University of Saskatchewan to advance a novel method for...
Nanopores feel the heat
Feb 16, 2022 (Nanowerk News) Scientists from SANKEN (the Institute of Scientific and Industrial Research) at Osaka University measured the thermal effects of ionic flow through a nanopore using a thermocouple. They found that, under most conditions, both the current and heating power varied with applied voltage as predicted by...
Size matters in nanoparticle treatments of traumatic injuries
Feb 16, 2022 (Nanowerk News) Traumatic injuries are the leading cause of death in the U.S. among people 45 and under, and such injuries account for more than 3 million deaths per year worldwide. To reduce the death toll of such injuries, many researchers are working on injectable nanoparticles that...
Breakthrough in converting CO2 into fuel using solar energy
Feb 16, 2022 (Nanowerk News) A research team led by Lund University in Sweden has shown how solar power can convert carbon dioxide into fuel, by using advanced materials and ultra-fast laser spectroscopy. The breakthrough could be an important piece of the puzzle in reducing the levels of greenhouse gases...
Nano-engineered sealer leads to more durable concrete
Feb 16, 2022 (Nanowerk News) A nanomaterials-engineered penetrating sealer developed by Washington State University researchers is able to better protect concrete from moisture and salt – the two most damaging factors in crumbling concrete infrastructure in northern states. The novel sealer showed a 75% improvement in repelling water and a...