Mar 24, 2022 (Nanowerk News) Researchers from NYU Abu Dhabi’s (NYUAD) Center for Space Science have discovered a new set of waves in the Sun that, unexpectedly, appear to travel much faster than predicted by theory. In the study, Discovery of high-frequency-retrograde vorticity waves in the Sun, published in the...
Carbon-coated nickel enables fuel cell free of precious metals
Mar 24, 2022 (Nanowerk News) A nitrogen doped carbon-coated nickel anode can catalyze an essential reaction in hydrogen fuel cells at a fraction of the cost of the precious metals currently used, Cornell researchers have found. The new discovery could accelerate the widespread use of hydrogen fuel cells, which hold...
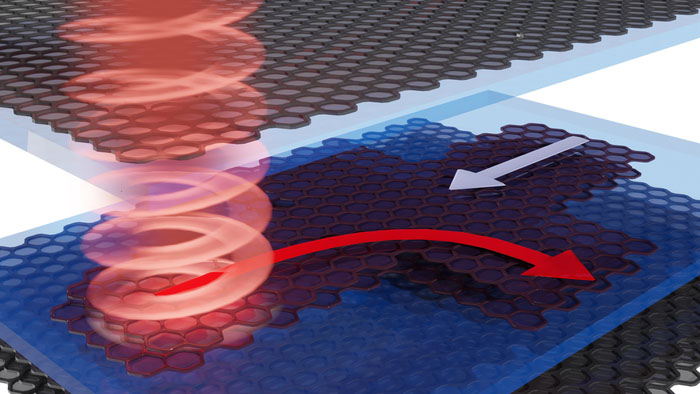
Light derails electrons through graphene (w/video)
Mar 24, 2022 (Nanowerk News) The way electrons flow in materials determine its electronic properties. For example, when a voltage is sustained across a conducting material, electrons start flowing, generating an electrical current. These electrons are often thought to flow in straight paths, moving along the electric field, much like...
Pivotal battery discovery could impact transportation and the grid
Mar 24, 2022 (Nanowerk News) Researchers uncover new avenue for overcoming the performance decline that occurs with repeated charge-discharge cycling in the cathodes of next generation batteries (Nature Communications, "Native lattice strain induced structural earthquake in sodium layered oxide cathodes"). Battery-powered vehicles have made a significant dent in the transportation...
Artificial intelligence to bring museum specimens to the masses
Mar 24, 2022 (Nanowerk News) Scientists are using cutting-edge artificial intelligence to help extract complex information from large collections of museum specimens. A team from Cardiff University is using state-of-the-art techniques to automatically segment and capture information from museum specimens and perform important data quality improvement without the need of...
Getting warmer: Improving heat flux modeling
Mar 24, 2022 (Nanowerk News) Scientists at Osaka University have simulated heat transport at the smallest scales using a molecular dynamics computer simulation. By studying the motions of the individual particles that make up the boundary between a solid and a liquid, they have been able to calculate heat flux...
Artificial intelligence based on ‘competing’ enzymes
Mar 24, 2022 (Nanowerk News) How do living cells compute? What do calculation and computing actually mean in nature? In his scientific work on chemical reaction networks, Albert Wong does not avoid these fundamental and rather philosophical questions. At the same time, he is working on basic interactions between enzymes...
Quantum optics offers topological matter even more protection
Mar 24, 2022 (Nanowerk News) Quantum optics might offer a way to make a class of exotic materials known as topological materials even more robust against defects, theoretical physicists at RIKEN have shown (Physical Review Letters, "Dissipative topological phase transition with strong system-environment coupling"). This finding could benefit the development...
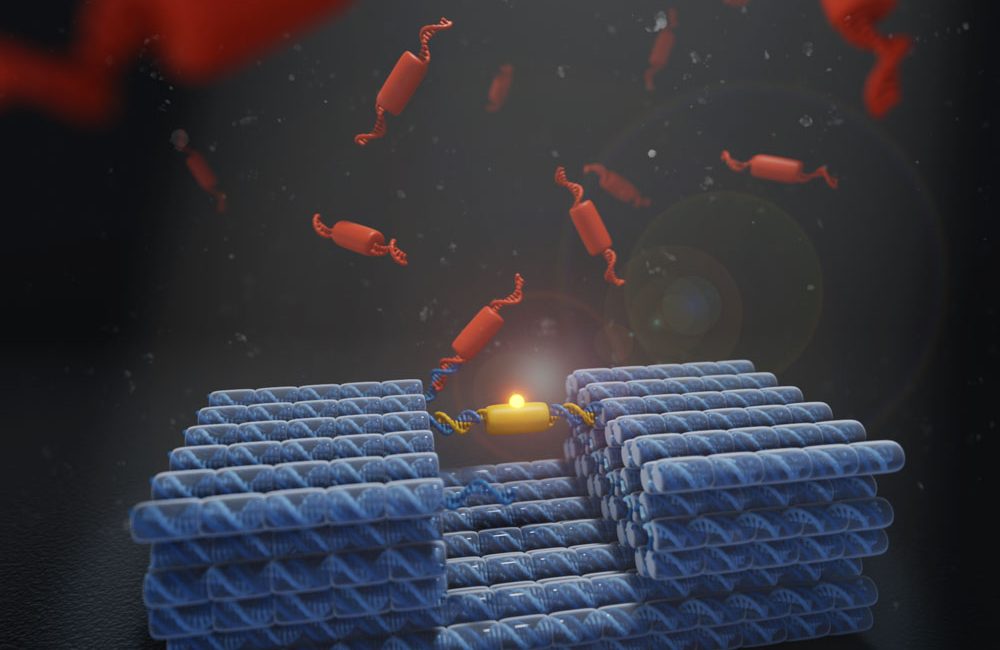
Autonomous nanomachines inspired by nature
Mar 23, 2022 (Nanowerk News) Inspired by the way molecules interact in nature, UNSW medical researchers engineer versatile nanoscale machines to enable greater functional range. To withstand the challenging conditions within living organisms, molecular machines need to be durably constructed for continuous operation over long periods. At the same time,...
Artificial intelligence tool may help predict heart attacks
Mar 23, 2022 (Nanowerk News) Investigators from Cedars-Sinai have created an artificial intelligence-enabled tool that may make it easier to predict if a person will have a heart attack. The tool, described in The Lancet Digital Health ("Deep learning-enabled coronary CT angiography for plaque and stenosis quantification and cardiac risk...