Mar 07, 2024 (Nanowerk News) Researchers from Carnegie Mellon University and Los Alamos National Laboratory have used machine learning to create a model that can simulate reactive processes in a diverse set of organic materials and conditions. "It's a tool that can be used to investigate more reactions in this...
Transparent wood with colorful and long-lasting room-temperature phosphorescence enables novel applications
Mar 07, 2024 (Nanowerk Spotlight) In the quest for sustainable and multifunctional materials, wood has emerged as a prime candidate due to its unique combination of strength, durability, and renewability. However, despite its many desirable properties, wood has long been hindered by its opacity, limiting its potential applications in fields...
Underwater touchscreen with self-powered luminescent particles
Mar 07, 2024 (Nanowerk News) Optical properties of afterglow luminescent particles (ALPs) in mechanoluminescence (ML) and mechanical quenching (MQ) have attracted great attention for diverse technological applications. Recently, a team of researchers from Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) has garnered attention by developing an optical display technology with...
Nanodevices can produce energy from evaporating tap or seawater
Mar 06, 2024 (Nanowerk News) Evaporation is a natural process so ubiquitous that most of us take it for granted. In fact, roughly half of the solar energy that reaches the earth drives evaporative processes. Since 2017, researchers have been working to harness the energy potential of evaporation via the...
New Nano-microscope enables simultaneous measurement of nanocomposite material properties
Mar 06, 2024 (Nanowerk News) The Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science (KRISS) has developed a hybrid nano-microscope capable of simultaneously measuring various nanomaterial properties. This nano-microscope is essential for researching the properties of nanocomposite materials and is also suitable for commercialization. It is expected to promote the development...
‘Ruler for light’ could enable detailed measurement in personal devices
Mar 06, 2024 (Nanowerk News) Stanford researchers have unveiled a new type of frequency comb, a high-precision measurement device, that is innovatively small, ultra-energy efficient, and exceptionally accurate. With continued development, this breakthrough “microcomb” – which is detailed in a study published in Nature ("Integrated frequency-modulated optical parametric oscillator") –...
New hydrogen producing method is simpler and safer
Mar 06, 2024 (Nanowerk News) Researchers in Sweden unveiled a new concept for producing hydrogen energy more efficiently, splitting water into oxygen and hydrogen without the dangerous risk of mixing the two gases. Developed at KTH Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm, the new method decouples the standard electrolysis process...
Metal-organic framework nanoparticles make vaccines more powerful
Mar 06, 2024 (Nanowerk News) Many vaccines, including vaccines for hepatitis B and whooping cough, consist of fragments of viral or bacterial proteins. These vaccines often include other molecules called adjuvants, which help to boost the immune system’s response to the protein. Most of these adjuvants consist of aluminum salts...
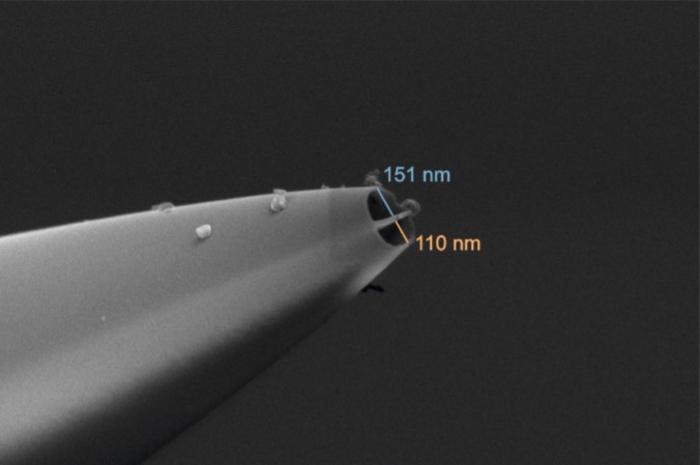
Nanosurgical tool could be key to cancer breakthrough
Mar 06, 2024 (Nanowerk News) The high-tech double-barrel nanopipette, developed by University of Leeds scientists, and applied to the global medical challenge of cancer, has - for the first time - enabled researchers to see how individual living cancer cells react to treatment and change over time – providing vital...
Discovery tests theory on cooling of white dwarf stars
Mar 06, 2024 (Nanowerk News) Open any astronomy textbook to the section on white dwarf stars and you’ll likely learn that they are “dead stars” that continuously cool down over time. New research published in Nature ("Buoyant crystals halt the cooling of white dwarf stars") is challenging this theory, with...