Mar 20, 2024 (Nanowerk News) Scientists have for the first time created a giant quantum vortex to mimic a black hole in superfluid helium that has allowed them to see in greater detail how analogue black holes behave and interact with their surroundings. Research led by the University of Nottingham,...
Twin stars reveal planet-eating habits
Mar 20, 2024 (Nanowerk News) At least one in a dozen stars show evidence of planetary ingestion according to a paper published in Nature ("At least one in a dozen stars shows evidence of planetary ingestion"). The international research team studied twin stars that should have identical composition. But, in...
iWood technology – integrating tactile sensing with natural wood for smart, responsive environments
Mar 20, 2024 (Nanowerk Spotlight) Wood is one of the oldest and most ubiquitous materials used by humans, with applications spanning construction, furniture, flooring, and beyond. For centuries, wood has served as the interface through which we interact with our built environment. However, while wood excels in its mechanical and...
X-Ray activated nanoparticles halt Alzheimer’s in study
Mar 20, 2024 (Nanowerk News) A novel approach in the field of Alzheimer’s research is emerging that could potentially transform how we tackle this debilitating disease. Recent studies have revealed a paradigm shift in understanding Alzheimer’s pathology, emphasizing the importance of targeting the early-stage aggregation of the pathogenic amyloid beta...
Safer quantum dots in medicine and water purification
Mar 20, 2024 (Nanowerk News) The 2023 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was focused on quantum dots — objects so tiny, they’re controlled by the strange and complex rules of quantum physics. Many quantum dots used in electronics are made from toxic substances, but their nontoxic counterparts are now being developed...
Heat used to transform antiskyrmions to skyrmions and back
Mar 19, 2024 (Nanowerk News) In an experiment that could help the development of new spintronics devices with low energy consumption, researchers from RIKEN and collaborators have used heat and magnetic fields to create transformations between spin textures—magnetic vortices and antivortices known as skyrmions and antiskyrmions — in a single...
A simple, scalable method using light to 3D print helical nanostructures
Mar 19, 2024 (Nanowerk News) A new fabrication process for helical metal nanoparticles provides a simpler, cheaper way to rapidly produce a material essential for biomedical and optical devices, according to a study by University of Michigan researchers. “One of our motivators is to drastically simplify manufacturing of complex materials...
Advanced hologram protection to combat counterfeiting
Mar 19, 2024 (Nanowerk News) Counterfeiting of various documents, banknotes, or tickets is a common problem that can be encountered in everyday life, even when shopping. Recognising the scale and seriousness of the problem, researchers at Kaunas University of Technology (KTU), Lithuania, decided to look for ways to further reduce...
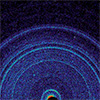
Higher intensity x-ray beams don’t always give stronger diffraction patterns
Mar 19, 2024 (Nanowerk News) Turning up the intensity of x-ray beams used to probe the atomic structures of materials can actually reduce the intensity of x-rays scattered from the material, a RIKEN-led team has found. This rather counterintuitive result could be harnessed to produce ultrashort pulses of x-rays. Scientists...
High-quality microwave signals generated from tiny photonic chip
Mar 19, 2024 (Nanowerk News) In a new Nature study ("All-optical frequency division on-chip using a single laser"), Columbia Engineering researchers have built a photonic chip that is able to produce high-quality, ultra-low-noise microwave signals using only a single laser. The compact device — a chip so small, it could...