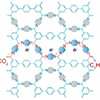
May 23, 2024 (Nanowerk News) Use of the greenhouse gas CO2 as a chemical raw material would not only reduce emissions, but also the consumption of fossil feedstocks. A novel metal-free organic framework could make it possible to electrocatalytically produce ethylene, a primary chemical raw material, from CO2. As a...
Researchers develop a novel strategy for growing two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides
May 23, 2024 (Nanowerk News) Two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides (2D TMDs) exhibit various polymorphic structures, including 2H (trigonal prismatic), 1T (octahedral), 1T′ and Td phases. These phases confer a range of properties such as superconductivity, ferroelectricity and ferromagnetism. By manipulating these structural phases, the rich physical properties of TMDs can...
3D printed conducting polymer hydrogels enable advanced implantable bioelectronics
May 23, 2024 (Nanowerk Spotlight) Implantable bioelectronic devices have immense potential for monitoring and treating a wide range of medical conditions by interfacing directly with biological tissues and organs. However, conventional rigid electronics often have a significant mechanical mismatch with soft, wet tissues, leading to poor signal quality, tissue damage,...
Quantum photonic technologies set to be more reliable with new interferometer
May 23, 2024 (Nanowerk News) An increasing number of emerging quantum applications operate using optical technologies. Essentially, photons carry information at the speed of light and over long distances, making them good candidates for fast and secure communications and quantum computing. Many of these applications require photons that are identical...
Could corrosion actually be helpful? New 3D printing technique might turn oxidation into an advantage
May 23, 2024 (Nanowerk News) New research from Binghamton University, State University of New York could revolutionize 3D printing and how engineers think about oxidation. When designing a mechanical system that includes metal, the engineer’s biggest enemy can be oxidation. The chemical reaction forms rust or causes other kinds of...
Flexible, biodegradable bioelectronic paper for personalized wireless stimulation implants
May 22, 2024 (Nanowerk News) A research team, jointly led by Professors Jiyun Kim, Chaenyung Cha, and Myoung Hoon Song from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at UNIST, has unveiled the world’s first flexible, biodegradable bioelectronic paper with homogeneously distributed wireless stimulation functionality for simple personalization of bioelectronic...
Controlling the chaos of active fluids
May 22, 2024 (Nanowerk News) Physicists at UC Santa Barbara, with colleagues at University of Michigan (UM) and The University of Chicago (UChicago), have developed design rules that take advantage of topological defects to control self-sustained chaotic flows in active fluids. This framework, for now developed as a theoretical model,...
Nanostrings that can vibrate forever (kind of)
May 22, 2024 (Nanowerk News) Researchers from TU Delft and Brown University have engineered string-like resonators capable of vibrating longer at ambient temperature than any previously known solid-state object — approaching what is currently only achievable near absolute zero temperatures. Their study, published in Nature Communications ("Centimeter-scale nanomechanical resonators with...
Ultra-flexible electronic slime takes cues from shape-shifting amoeba
May 22, 2024 (Nanowerk Spotlight) The field of epidermal electronics, which involves flexible electronic systems that interface with the skin, has attracted growing interest in recent years for potential applications ranging from health monitoring to human-machine interaction. However, widespread adoption has been hindered by limitations in existing technologies, including complex...
Researchers develop a MOF detector for continuously monitoring toxic gases
May 22, 2024 (Nanowerk News) Most systems used to detect toxic gases in industrial or domestic settings can be used only once, or at best a few times. Now, researchers at MIT have developed a detector that could provide continuous monitoring for the presence of these gases, at low cost....