Sep 16, 2024 (Nanowerk Spotlight) Ammonia, a compound often associated with foul odors, is far more than an inconvenience – it’s a vital indicator of processes as diverse as food spoilage, environmental pollution, and even human metabolic disorders. As meat such as beef deteriorates, it emits gases like ammonia, a...
Using sunlight to turn two greenhouse gases into valuable chemicals
Sep 16, 2024 (Nanowerk News) McGill University researchers have harnessed the power of sunlight to transform two of the most harmful greenhouse gases into valuable chemicals. The discovery could help combat climate change and provide a more sustainable way to produce certain industrial products. “Imagine a world where the exhaust...
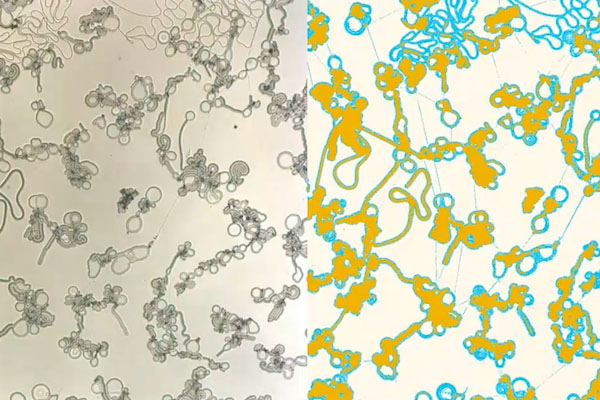
Liquid crystals in motion mimic biological systems
Sep 16, 2024 (Nanowerk News) Liquid crystals are all around us, from cell phone screens and video game consoles to car dashboards and medical devices. Run an electric current through liquid crystal displays (LCDs) and they generate colors, thanks to the unique properties of these fluids: rearrange their shape, and...
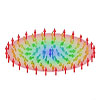
Energy-saving computing with magnetic whirls
Sep 16, 2024 (Nanowerk News) Researchers at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) have managed to enhance the framework of Brownian reservoir computing by recording and transferring hand gestures to the system which then used skyrmions to detect these individual gestures. "We were impressed to see that our hardware approach and...
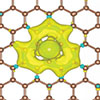
Controlling molecular arrangements using selenium doping
Sep 16, 2024 (Nanowerk News) Physicists from the National University of Singapore (NUS) have achieved controlled conformational arrangements in nanostructures using a flexible precursor and selenium doping, enhancing material properties and structural homogeneity. Their method advances on-surface synthesis for the design and development of engineered nanomaterials. On-surface synthesis has been...
Astronomers detect black hole ‘starving’ its host galaxy to death
Sep 16, 2024 (Nanowerk News) Astronomers have used the NASA/ESA James Webb Space Telescope to confirm that supermassive black holes can starve their host galaxies of the fuel they need to form new stars. The international team, co-led by the University of Cambridge, used Webb to observe a galaxy roughly...