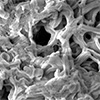
Dec 18, 2024 (Nanowerk News) Using a chemical reaction inspired by rocket fuel ignition, Cornell researchers have engineered a nanoporous carbon with the highest surface area ever reported, a breakthrough that is already proving beneficial for carbon-dioxide capture and energy storage technologies. Scientists are continually striving to enhance the porosity...
Microrobots and the ‘lazy agent problem’
Dec 19, 2024 (Nanowerk News) Imagine trying to move a heavy piece of furniture with a group of people. Everyone’s effort matters, but how do you ensure that each person is pulling their weight? This challenge of fairly distributing the load is a critical issue not only in human teamwork...
Photons dance like pieces on a Go board
Dec 19, 2024 (Nanowerk News) In everyday life, light is a wave as is apparent from the colorful iridescence of opal gemstones, or from oil films on water puddles. We also take it for granted that light travels in all directions. Recently, however, scientists from the Universities of Twente, Copenhagen,...
This prototype sunscreen protects your skin and cools you off, too
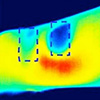
Dec 19, 2024 (Nanowerk News) Wearing sunscreen is important to protect your skin from the harmful effects of UV radiation but doesn’t cool people off. However, a new formula, described in Nano Letters ("High-Performance Radiative Cooling Sunscreen"), protects against both UV light and heat from the sun using radiative cooling....
Tinkering with the ‘clockwork’ mechanisms of life
Dec 19, 2024 (Nanowerk News) Living organisms monitor time – and react to it – in many different ways, from detecting light and sound in microseconds to responding physiologically in pre-programmed ways, via their daily sleep cycle, monthly menstrual cycle, or to changes in the seasons. Such ability to react...
Bacteria-infused, living ceramic materials remove carbon dioxide and detect toxic gases
Dec 19, 2024 (Nanowerk Spotlight) Nature has perfected what human engineering still struggles to achieve: creating materials that can adapt, sense their environment, and transform harmful substances into useful ones. While modern materials science has produced remarkable synthetic materials, from superstrong alloys to smart polymers, these materials lack the dynamic...
Unlocking new insights into in-plane magnetic field-induced hall effects
Dec 19, 2024 (Nanowerk News) In-plane magnetic fields are responsible for inducing anomalous Hall effect in EuCd2Sb2 films, report researchers from the Institute of Science Tokyo. By studying how these fields change electronic structures, the team discovered a large in-plane anomalous Hall effect. These findings pave the way for new...
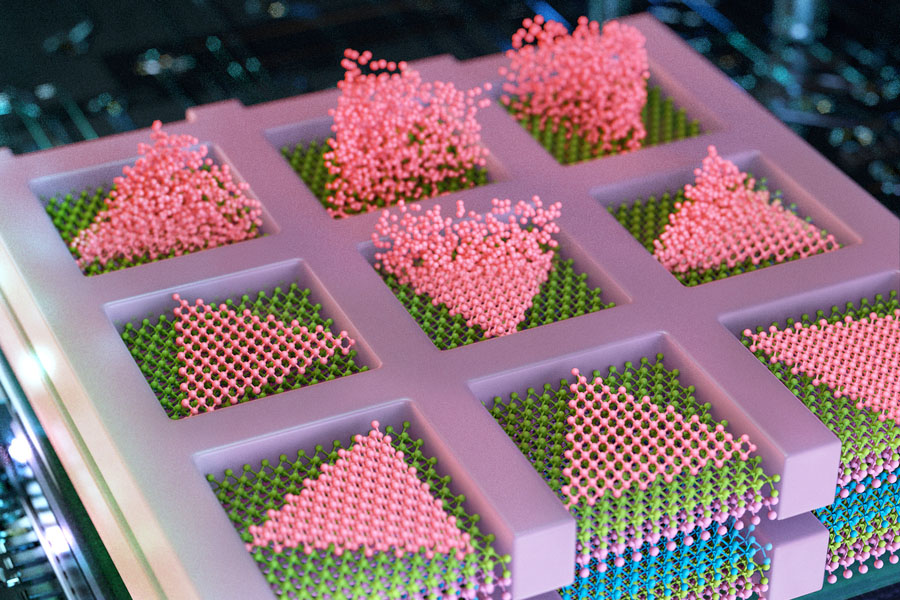
Engineers grow ‘high-rise’ 3D chips
Dec 19, 2024 (Nanowerk News) The electronics industry is approaching a limit to the number of transistors that can be packed onto the surface of a computer chip. So, chip manufacturers are looking to build up rather than out. Instead of squeezing ever-smaller transistors onto a single surface, the industry...
Physicists magnetize a material with light
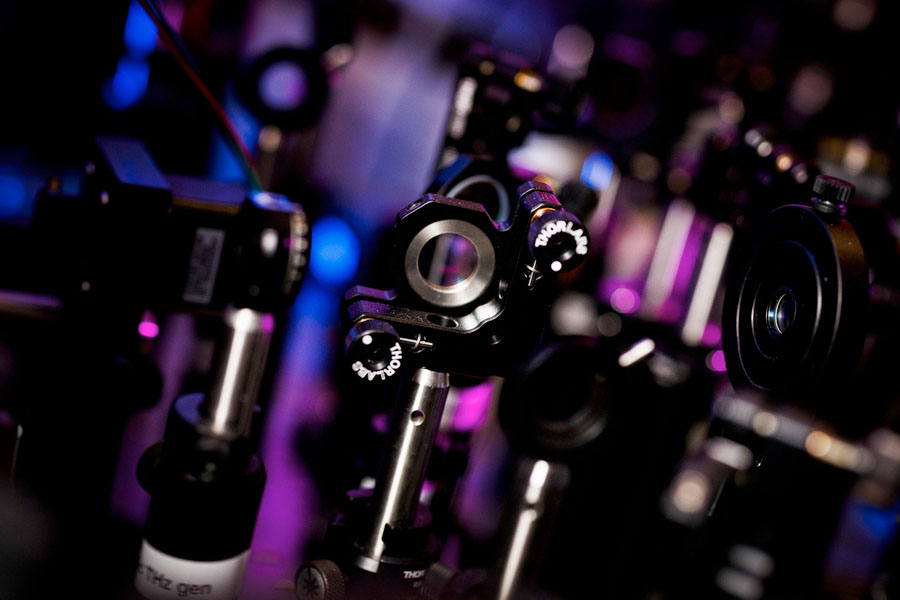
Dec 19, 2024 (Nanowerk News) MIT physicists have created a new and long-lasting magnetic state in a material, using only light. In a study appearing in Nature ("Terahertz field-induced metastable magnetization near criticality in FePS3"), the researchers report using a terahertz laser — a light source that oscillates more than...
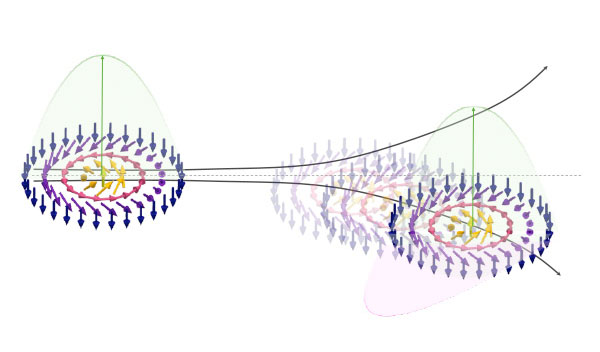
The motion of magnetic whirlpools is all relative
Dec 19, 2024 (Nanowerk News) The future storage and processing of data stand to benefit greatly from tiny magnetic whirlpools known as skyrmions, which are robust against noise and may be useful in lower power consumption devices. The development of skyrmion-based technologies has received a boost from a simple and...