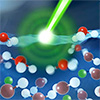
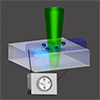
Apr 25, 2025 Researchers used a light-based technique to observe the fast formation of electrical double layers, validating models for membranes and energy storage devices. (Nanowerk News) Charged surfaces in contact with liquids – such as biological cell walls or battery electrodes – attract oppositely charged ions from the liquid....
Structure dictates effectiveness, safety in nanomedicine
Apr 25, 2025 Structural precision drives therapeutic innovation, ultimately benefiting patients. (Nanowerk News) Historically, the vast majority of pharmaceutical drugs have been meticulously designed down to the atomic level. The specific location of each atom within the drug molecule is a critical factor in determining how well it works and...
Polydopamine nanoparticles enable precise light-driven activation of neurons and muscles
Apr 25, 2025 Researchers use biocompatible polydopamine nanoparticles and near-infrared light to remotely trigger activity in neuron and muscle cells with minimal side effects. (Nanowerk Spotlight) Remote control over the behavior of individual cells has remained one of the more difficult problems in neuroscience and muscle physiology. The ability to...
Astronomers find Earth-like exoplanets common across the cosmos
Apr 25, 2025 New study debunks a single planet-formation scenario. (Nanowerk News) Using the Korea Microlensing Telescope Network (KMTNet), an international team of researchers has discovered that super-Earth exoplanets are more common across the universe than previously thought, according to a new study. By studying light anomalies made by the...
The ‘spacecraft speedometer’ is a new, innovative way to track satellites
Apr 25, 2025 A new instrument can predict satellite location without the use of GPS. (Nanowerk News) Researchers at Los Alamos National Laboratory and the United States Air Force Academy have developed a novel instrument called the Spacecraft Speedometer — a compact, resource-efficient device — capable of determining the velocity...
An earth-abundant mineral for sustainable spintronics
Apr 25, 2025 Iron-rich hematite, commonly found in rocks and soil, turns out to have magnetic properties that make it a promising material for ultrafast next-generation computing. (Nanowerk News) In 2023, EPFL researchers succeeded in sending and storing data using charge-free magnetic waves called spin waves, rather than traditional electron...