Home > Press > Data can now be processed at the speed of light!
 |
| Research Image
CREDIT POSTECH |
Abstract:
How can Marvel movie character Ant-Man produce such strong energy out of his small body? The secret lies in the transistors on his suit that amplify weak signals for processing. Transistors that amplify electrical signals in the conventional way lose heat energy and limit the speed of signal transfer, which degrades performance. What if it were possible to overcome such limitation and make a high-performance suit that is light and small but without loss of heat energy?
Data can now be processed at the speed of light!
Pohang, South Korea | Posted on April 14th, 2023
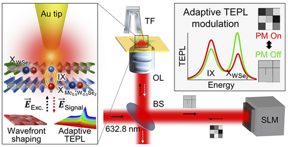
A POSTECH team of Professor Kyoung-Duck Park and Yeonjeong Koo from the Department of Physics and a team from ITMO University in Russia led by Professor Vasily Kravtsov jointly developed a nano-excitonic transistor using intralayer and interlayer excitons in heterostructure-based semiconductors, which addresses the limitations of existing transistors.
Excitons are responsible for light emission of semiconductor materials and are key to developing a next-generation light-emitting element with less heat generation and a light source for quantum information technology due to the free conversion between light and material in their electrically neutral states. There are two types of excitons in a semiconductor heterobilayer, which is a stack of two different semiconductor monolayers: the intralayer excitons with horizontal direction and the interlayer excitons with vertical direction.
Optical signals emitted by the two excitons have different lights, durations, and coherence times. This means that selective control of the two optical signals could enable the development of a two-bit exciton transistor. However, it was challenging to control intra- and interlayer excitons in nano-scale spaces due to the non-homogeneity of semiconductor heterostructures and low luminous efficiency of interlayer excitons in addition to the diffraction limit of light.
The team in its previous research had proposed technology for controlling excitons in nano-level spaces by pressing semiconductor materials with a nano-scale tip. This time, for the first time ever, the researchers were able to remotely control the density and luminance efficiency of excitons based on polarized light on the tip without directly touching the excitons. The most significant advantage of this method, which combines a photonic nanocavity and a spatial light modulator, is that it can reversibly control excitons, minimizing physical damage to the semiconductor material. Also, the nano-excitonic transistor that utilizes light can help process massive amounts of data at the speed of light while minimizing heat energy loss.
Artificial intelligence (AI) has made inroads into our lives more quickly than we ever expected, and it requires huge volumes of data for learning in order to provide good answers that are actually helpful for users. The ever-increasing volume of information should be collected and processed as more and more fields utilize AI. This research is expected to propose a new data processing strategy befitting an era of data explosion. Yeonjeong Koo, one of the co-first authors of the research paper, said, The nano-excitonic transistor is expected to play an integral role in realizing an optical computer, which will help process the huge amounts of data driven by AI technology.
The research, recently published in international journal ACS Nano, was supported by the Samsung Science and Technology Foundation and National Research Foundation of Korea.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jinyoung Huh
Pohang University of Science & Technology (POSTECH)
Office: 82-54-279-2415
Copyright © Pohang University of Science & Technology (POSTECH)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
News and information
![]()
New family of wheel-like metallic clusters exhibit unique properties April 14th, 2023
![]()
Efficient heat dissipation perovskite lasers using a high-thermal-conductivity diamond substrate April 14th, 2023
![]()
Nanobiotechnology: How Nanomaterials Can Solve Biological and Medical Problems April 14th, 2023
![]()
New Developments in Biosensor Technology: From Nanomaterials to Cancer Detection April 14th, 2023
Possible Futures
![]()
New family of wheel-like metallic clusters exhibit unique properties April 14th, 2023
![]()
Diamond cut precision: University of Illinois to develop diamond sensors for neutron experiment and quantum information science April 14th, 2023
![]()
Channeling mechanical energy in a preferred direction April 14th, 2023
![]()
Implantable device shrinks pancreatic tumors: Taming pancreatic cancer with intratumoral immunotherapy April 14th, 2023
Chip Technology
![]()
Graphene grows and we can see it March 24th, 2023
![]()
Optical switching at record speeds opens door for ultrafast, light-based electronics and computers: March 24th, 2023
![]()
Semiconductor lattice marries electrons and magnetic moments March 24th, 2023
![]()
Light meets deep learning: computing fast enough for next-gen AI March 24th, 2023
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]()
Efficient heat dissipation perovskite lasers using a high-thermal-conductivity diamond substrate April 14th, 2023
![]()
Optical switching at record speeds opens door for ultrafast, light-based electronics and computers: March 24th, 2023
![]()
Light meets deep learning: computing fast enough for next-gen AI March 24th, 2023
![]()
New study opens the door to ultrafast 2D devices that use nonequilibrium exciton superdiffusion February 10th, 2023
Discoveries
![]()
Efficient heat dissipation perovskite lasers using a high-thermal-conductivity diamond substrate April 14th, 2023
![]()
Diamond cut precision: University of Illinois to develop diamond sensors for neutron experiment and quantum information science April 14th, 2023
![]()
Channeling mechanical energy in a preferred direction April 14th, 2023
![]()
Implantable device shrinks pancreatic tumors: Taming pancreatic cancer with intratumoral immunotherapy April 14th, 2023
Announcements
![]()
Nanobiotechnology: How Nanomaterials Can Solve Biological and Medical Problems April 14th, 2023
![]()
New Developments in Biosensor Technology: From Nanomaterials to Cancer Detection April 14th, 2023
![]()
IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
![]()
Diamond cut precision: University of Illinois to develop diamond sensors for neutron experiment and quantum information science April 14th, 2023
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]()
New family of wheel-like metallic clusters exhibit unique properties April 14th, 2023
![]()
Efficient heat dissipation perovskite lasers using a high-thermal-conductivity diamond substrate April 14th, 2023
![]()
Diamond cut precision: University of Illinois to develop diamond sensors for neutron experiment and quantum information science April 14th, 2023
![]()
Channeling mechanical energy in a preferred direction April 14th, 2023
Artificial Intelligence
![]()
Light meets deep learning: computing fast enough for next-gen AI March 24th, 2023
![]()
3D-printed decoder, AI-enabled image compression could enable higher-res displays December 9th, 2022
![]()
New chip ramps up AI computing efficiency August 19th, 2022
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]()
Efficient heat dissipation perovskite lasers using a high-thermal-conductivity diamond substrate April 14th, 2023
![]()
Optical switching at record speeds opens door for ultrafast, light-based electronics and computers: March 24th, 2023
![]()
Light meets deep learning: computing fast enough for next-gen AI March 24th, 2023










