Home > Press > Round nanoparticles improve quality factors of surface lattice resonances: Study
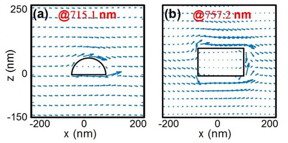 |
| An energy flux propagates along a surface and bypasses the nanoparticle at SLR. The hemisphere shape introduces weaker perturbations than the rod shape, resulting in much lower loss and a much higher quality factor.
CREDIT SIAT |
Abstract:
Plasmonic surface lattice resonances (SLRs) supported by metal nanoparticle arrays have many merits such as strong field enhancements extended over large volumes, as well as long lifetimes, narrow linewidths, angle-dependent dispersion, and a wide range of wavelength tunability.
Round nanoparticles improve quality factors of surface lattice resonances: Study
Beijing, China | Posted on August 28th, 2020
This study was published in Nature Photonics on August 10.
To reach atomic resolution with light has always been one of the ultimate goals in nano-optics. The advent of scanning near-field optical microscopy (SNOM) kindled hopes for the goal.
Prof. DONG and his colleagues successfully demonstrated sub-nanometer scale spatial resolution in the single-molecule Raman spectroscopy imaging with local enhancement effect of a nanocavity plasmon field in a study in 2013.
However, unlike the Raman scattering process, fluorescence will be quenched in the very immediate vicinity of metals which stops the resolution development of SNOM at around 10 nm.
The radiation properties (fluorescence) of molecules in the metal nanocavity are directly affected by the photon density of the nanocavity , and the photon density of the nanocavity is closely related to the structure of the probe tip. Therefore, it is the key to modify the structure of the probe and the electronic state of the molecules in the nanocavity to avoid the fluorescence quenching and achieve high-resolution photofluorescence imaging.
DONG’s team further fine-tuned the plasmon nanocavity, especially in the fabrication and control of the atomic-level structure of the probe tip. They constructed an Ag tip apex with an atomistic protrusion and matched the nanocavity plasmon resonance with the effective energy of the incident laser and molecular luminescence.
Then, the researchers used an ultra-thin dielectric layer (three-atom-thick NaCl) to isolate the charge transfer between the nanocavity molecules and the metal substrate, achieving sub-nanometer resolution of the single-molecule photoluminescence imaging.
They found that with the probe approaching the molecule, even if their distance is less than 1 nm, the intensity of photoluminescence continues increasing monotonously. And the fluorescence quenching disappears completely.
Theoretical simulations showed that when the atomistic protrusion tip and the metal substrate form a plasmon nanocavity, the resonance response of the nanocavity plasmon and the lightning rod effect of the atomistic protrusion structure would have a synergistic effect. The synergistic effect generates a strong and highly localized electromagnetic field compressing the cavity mode volume to below 1 nm3, which greatly increases the localized photon density of states and the molecular radiation decay rate. These effects not only inhibit the fluorescence quenching, but also realize sub-nanometer-resolution photoluminescence imaging.
To achieve sub-nanometer spatial resolution, the size of the tip and the distance between the tip and the sample must be on the sub-nanometer scale.
The researchers further realized sub-molecular-resolved photoluminescence hyperspectral imaging with spectral information, and demonstrated the effects of local plasmon-exciton interaction on fluorescence intensity, peak position and peak width on the sub-nanometer scale.
This research achieved the long-awaited goal of using light to analyze the internal structure of molecules in SNOM, and provided a new technical method for detecting and modulating the localized environment of molecules and light-matter interactions on the sub-nanometer scale.
The reviewers of Nature Photonics say that this paper will be an important article in its field, which has guiding significance for carrying out ultra-sensitive spectroscopic microscopy research with atomic-scale light.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
ZHANG Xiaomin
Copyright © Chinese Academy of Sciences Headquarters
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
News and information
![]() Machine learning peeks into nano-aquariums August 31st, 2020
Machine learning peeks into nano-aquariums August 31st, 2020
![]() Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
![]() Observation charge accumulation at nanocavity on plasmonic photocatalyst August 28th, 2020
Observation charge accumulation at nanocavity on plasmonic photocatalyst August 28th, 2020
Imaging
![]() Machine learning peeks into nano-aquariums August 31st, 2020
Machine learning peeks into nano-aquariums August 31st, 2020
Possible Futures
![]() Machine learning peeks into nano-aquariums August 31st, 2020
Machine learning peeks into nano-aquariums August 31st, 2020
![]() Observation charge accumulation at nanocavity on plasmonic photocatalyst August 28th, 2020
Observation charge accumulation at nanocavity on plasmonic photocatalyst August 28th, 2020
![]() Optical imaging enters sub-nanometer era August 28th, 2020
Optical imaging enters sub-nanometer era August 28th, 2020
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() A powder method for the high-efficacy measurement of electro-optic coefficients August 21st, 2020
A powder method for the high-efficacy measurement of electro-optic coefficients August 21st, 2020
Discoveries
![]() Machine learning peeks into nano-aquariums August 31st, 2020
Machine learning peeks into nano-aquariums August 31st, 2020
![]() Optical imaging enters sub-nanometer era August 28th, 2020
Optical imaging enters sub-nanometer era August 28th, 2020
![]() Arrowhead and Collaborator Janssen Present Phase 2 Clinical Data on Investigational Hepatitis B Therapeutic JNJ-3989 at The Digital Liver Congress August 28th, 2020
Arrowhead and Collaborator Janssen Present Phase 2 Clinical Data on Investigational Hepatitis B Therapeutic JNJ-3989 at The Digital Liver Congress August 28th, 2020
Announcements
![]() Machine learning peeks into nano-aquariums August 31st, 2020
Machine learning peeks into nano-aquariums August 31st, 2020
![]() Optical imaging enters sub-nanometer era August 28th, 2020
Optical imaging enters sub-nanometer era August 28th, 2020
![]() Arrowhead and Collaborator Janssen Present Phase 2 Clinical Data on Investigational Hepatitis B Therapeutic JNJ-3989 at The Digital Liver Congress August 28th, 2020
Arrowhead and Collaborator Janssen Present Phase 2 Clinical Data on Investigational Hepatitis B Therapeutic JNJ-3989 at The Digital Liver Congress August 28th, 2020
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Machine learning peeks into nano-aquariums August 31st, 2020
Machine learning peeks into nano-aquariums August 31st, 2020
![]() Observation charge accumulation at nanocavity on plasmonic photocatalyst August 28th, 2020
Observation charge accumulation at nanocavity on plasmonic photocatalyst August 28th, 2020
![]() Optical imaging enters sub-nanometer era August 28th, 2020
Optical imaging enters sub-nanometer era August 28th, 2020
Tools
![]() Machine learning peeks into nano-aquariums August 31st, 2020
Machine learning peeks into nano-aquariums August 31st, 2020
![]() Optical imaging enters sub-nanometer era August 28th, 2020
Optical imaging enters sub-nanometer era August 28th, 2020
![]() New super-resolution method reveals fine details without constantly needing to zoom in August 12th, 2020
New super-resolution method reveals fine details without constantly needing to zoom in August 12th, 2020
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() A powder method for the high-efficacy measurement of electro-optic coefficients August 21st, 2020
A powder method for the high-efficacy measurement of electro-optic coefficients August 21st, 2020
![]() Monolayer transition metal dichalcogenide lens for high resolution imaging August 14th, 2020
Monolayer transition metal dichalcogenide lens for high resolution imaging August 14th, 2020










