Home > Press > Quantum quirk yields giant magnetic effect, where none should exist: Study opens window into the landscape of extreme topological matter
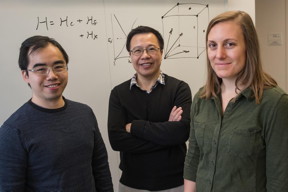 |
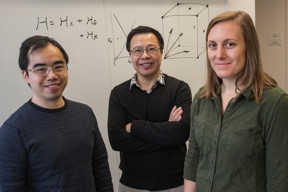
| Rice University theoretical physicists (from left) Hsin-Hua Lai, Qimiao Si and Sarah Grefe worked with experimental collaborators at Vienna University of Technology to understand topological features of a nonmagnetic Weyl-Kondo semimetal allowed it to produce a giant Hall effect in the absence of a magnetic field.
CREDIT Photo by Jeff Fitlow/Rice University |
Abstract:
In a twist befitting the strange nature of quantum mechanics, physicists have discovered the Hall effect — a characteristic change in the way electricity is conducted in the presence of a magnetic field — in a nonmagnetic quantum material to which no magnetic field was applied.
Quantum quirk yields giant magnetic effect, where none should exist: Study opens window into the landscape of extreme topological matter
Houston, TX | Posted on March 1st, 2021
The discovery by researchers from Rice University, Austria’s Vienna University of Technology (TU Wien), Switzerland’s Paul Scherrer Institute and Canada’s McMaster University is detailed in a paper in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Of interest are both the origins of the effect, which is typically associated with magnetism, and its gigantic magnitude — more than 1,000 times larger than one might observe in simple semiconductors.
Rice study co-author Qimiao Si, a theoretical physicist who has investigated quantum materials for nearly three decades, said, “It’s really topology at work,” referring to the patterns of quantum entanglement that give rise the unorthodox state.
The material, an exotic semimetal of cerium, bismuth and palladium, was created and measured at TU Wien by Silke Bühler-Paschen, a longtime collaborator of Si’s. In late 2017, Si, Bühler-Paschen and colleagues discovered a new type of quantum material they dubbed a “Weyl-Kondo semimetal.” The research laid the groundwork for empirical investigations, but Si said the experiments were challenging, in part because it wasn’t clear “which physical quantity would pick up the effect.”
In April 2018, Bühler-Paschen and TU Wien graduate student Sami Dzsaber, the study’s first author, dropped by Si’s office while attending a workshop at the Rice Center for Quantum Materials (RCQM). When Si saw Dzsaber’s data, he was dubious.
“Upon seeing this, everybody’s first reaction is that it is not possible,” he said.
To appreciate why, it helps to understand both the nature and the 1879 discovery of Edwin Hall, a doctoral student who found that applying a magnetic field at a 90-degree angle to conducting wire produced a voltage difference across the wire, in the direction perpendicular to both the current and the magnetic field. Physicists eventually discovered the source of the Hall effect: The magnetic field deflects the motion of passing electrons, pulling them toward one side of the wire. The Hall effect is a standard tool in physics labs, and devices that make use of it are found in products as diverse as rocket engines and paintball guns. Studies related to the quantum nature of the Hall effect captured Nobel Prizes in 1985 and 1998.
Dzsaber’s experimental data clearly showed a characteristic Hall signal, even though no magnetic field was applied.
“If you don’t apply a magnetic field, the electron is not supposed to bend,” Si said. “So, how could you ever get a voltage drop along the perpendicular direction? That’s why everyone didn’t believe this at first.”
Experiments at the Paul Scherrer Institute ruled out the presence of a tiny magnetic field that could only be detected on a microscopic scale. So the question remained: What caused the effect?
“In the end, all of us had to accept that this was connected to topology,” Si said.
In topological materials, patterns of quantum entanglement produce “protected” states, universal features that cannot be erased. The immutable nature of topological states is of increasing interest for quantum computing. Weyl semimetals, which manifest a quasiparticle known as the Weyl fermion, are topological materials.
So are the Weyl-Kondo semimetals Si, Bühler-Paschen and colleagues discovered in 2018. Those feature both Weyl fermions and the Kondo effect, an interaction between the magnetic moments of electrons attached to atoms inside the metal and the spins of passing conduction electrons.
“The Kondo effect is the quintessential form of strong correlations in quantum materials,” Si said in reference to the correlated, collective behavior of billions upon billions of quantum entangled particles. “It qualifies the Weyl-Kondo semimetal as one of the rare examples of a topological state that’s driven by strong correlations.
“Topology is a defining characteristic of the Weyl-Kondo semimetal, and the discovery of this spontaneous giant Hall effect is really the first detection of topology that’s associated with this kind of Weyl fermion,” Si said.
Experiments showed that the effect arose at the characteristic temperature associated with the Kondo effect, indicating the two are likely connected, Si said.
“This kind of spontaneous Hall effect was also observed in contemporaneous experiments in some layered semiconductors, but our effect is more than 1,000 times larger,” he said. “We were able to show that the observed giant effect is, in fact, natural when the topological state develops out of strong correlations.”
Si said the new observation is likely “a tip of the iceberg” of extreme responses that result from the interplay between strong correlations and topology.
He said the size of the topologically generated Hall effect is also likely to spur investigations into potential uses of the technology for quantum computation.
“This large magnitude, and its robust, bulk nature presents intriguing possibilities for exploitation in topological quantum devices,” Si said.
Si is the Harry C. and Olga K. Wiess Professor in Rice’s Department of Physics and Astronomy and director of RCQM. Bühler-Paschen is a professor at TU Wien’s Institute for Solid State Physics.
###
Study co-authors include Sarah Grefe and Hsin-Hua Lai, both of Rice; Xinlin Yan, Mathieu Taupin, Gaku Eguchi, Andrey Prokofiev and Peter Blaha of TU Wien; Toni Shiroka of the Paul Scherrer Institute; and Oleg Rubel of McMaster University.
The research was funded by the Austrian Science Fund (P29279-N27, P29296-N27, W1243), the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Program (EMP-824109), the Swiss National Science Foundation (200021-169455), the National Science Foundation (1920740, 1607611), the Welch Foundation (C-1411) and an Ulam Scholarship from the Center for Nonlinear Studies at Los Alamos National Laboratory.
RCQM leverages global partnerships and the strengths of more than 20 Rice research groups to address questions related to quantum materials. RCQM is supported by Rice’s offices of the provost and the vice provost for research, the Wiess School of Natural Sciences, the Brown School of Engineering, the Smalley-Curl Institute and the departments of Physics and Astronomy, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Materials Science and NanoEngineering.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation’s top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,978 undergraduates and 3,192 graduate students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is just under 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for lots of race/class interaction and No. 1 for quality of life by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger’s Personal Finance.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jade Boyd
713-348-6778
@RiceUNews
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
![]() A copy of the paper is available at:
A copy of the paper is available at:
News and information
![]() A COSMIC approach to nanoscale science: Instrument at Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Light Source achieves world-leading resolution of nanomaterials March 5th, 2021
A COSMIC approach to nanoscale science: Instrument at Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Light Source achieves world-leading resolution of nanomaterials March 5th, 2021
Laboratories
![]() A COSMIC approach to nanoscale science: Instrument at Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Light Source achieves world-leading resolution of nanomaterials March 5th, 2021
A COSMIC approach to nanoscale science: Instrument at Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Light Source achieves world-leading resolution of nanomaterials March 5th, 2021
![]() Discovery could lead to self-propelled robots February 2nd, 2021
Discovery could lead to self-propelled robots February 2nd, 2021
Quantum Physics
![]() Atomic nuclei in the quantum swing: The extremely precise control of nuclear excitations opens up possibilities of ultra-precise atomic clocks and powerful nuclear batteries February 19th, 2021
Atomic nuclei in the quantum swing: The extremely precise control of nuclear excitations opens up possibilities of ultra-precise atomic clocks and powerful nuclear batteries February 19th, 2021
![]() Quantum Optimization: Computer scientist Yufei Ding receives NSF Early CAREER Award to advance efforts to improve quantum applications January 21st, 2021
Quantum Optimization: Computer scientist Yufei Ding receives NSF Early CAREER Award to advance efforts to improve quantum applications January 21st, 2021
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() A COSMIC approach to nanoscale science: Instrument at Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Light Source achieves world-leading resolution of nanomaterials March 5th, 2021
A COSMIC approach to nanoscale science: Instrument at Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Light Source achieves world-leading resolution of nanomaterials March 5th, 2021
![]() Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals Files IND to Begin Phase 2b Study of ARO-APOC3 in Patients with Severe Hypertriglyceridemia March 2nd, 2021
Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals Files IND to Begin Phase 2b Study of ARO-APOC3 in Patients with Severe Hypertriglyceridemia March 2nd, 2021
![]() Bioinformatics tool accurately tracks synthetic: DNA Computer scientists show benefits of bioinformatics with PlasmidHawk February 26th, 2021
Bioinformatics tool accurately tracks synthetic: DNA Computer scientists show benefits of bioinformatics with PlasmidHawk February 26th, 2021
Possible Futures
![]() A COSMIC approach to nanoscale science: Instrument at Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Light Source achieves world-leading resolution of nanomaterials March 5th, 2021
A COSMIC approach to nanoscale science: Instrument at Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Light Source achieves world-leading resolution of nanomaterials March 5th, 2021
Chip Technology
![]() CEA-Leti Announces 16 Papers to Be Presented At Photonics West 2021 and a Virtual Workshop on March 25 March 3rd, 2021
CEA-Leti Announces 16 Papers to Be Presented At Photonics West 2021 and a Virtual Workshop on March 25 March 3rd, 2021
![]() Engineering the boundary between 2D and 3D materials: Cutting-edge microscope helps reveal ways to control the electronic properties of atomically thin materials February 26th, 2021
Engineering the boundary between 2D and 3D materials: Cutting-edge microscope helps reveal ways to control the electronic properties of atomically thin materials February 26th, 2021
Quantum Computing
![]() CEA-Leti Announces 16 Papers to Be Presented At Photonics West 2021 and a Virtual Workshop on March 25 March 3rd, 2021
CEA-Leti Announces 16 Papers to Be Presented At Photonics West 2021 and a Virtual Workshop on March 25 March 3rd, 2021
![]() Quantum computing: when ignorance is wanted February 19th, 2021
Quantum computing: when ignorance is wanted February 19th, 2021
Discoveries
![]() A COSMIC approach to nanoscale science: Instrument at Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Light Source achieves world-leading resolution of nanomaterials March 5th, 2021
A COSMIC approach to nanoscale science: Instrument at Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Light Source achieves world-leading resolution of nanomaterials March 5th, 2021
Materials/Metamaterials
![]() Expanding the freedom of design: powder coating on FRP thanks to conductive gelcoats with graphene nanotubes March 3rd, 2021
Expanding the freedom of design: powder coating on FRP thanks to conductive gelcoats with graphene nanotubes March 3rd, 2021
![]() Changing the silkworm’s diet to spin stronger silk February 26th, 2021
Changing the silkworm’s diet to spin stronger silk February 26th, 2021
Announcements
![]() A COSMIC approach to nanoscale science: Instrument at Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Light Source achieves world-leading resolution of nanomaterials March 5th, 2021
A COSMIC approach to nanoscale science: Instrument at Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Light Source achieves world-leading resolution of nanomaterials March 5th, 2021
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() A COSMIC approach to nanoscale science: Instrument at Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Light Source achieves world-leading resolution of nanomaterials March 5th, 2021
A COSMIC approach to nanoscale science: Instrument at Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Light Source achieves world-leading resolution of nanomaterials March 5th, 2021
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Bioinformatics tool accurately tracks synthetic: DNA Computer scientists show benefits of bioinformatics with PlasmidHawk February 26th, 2021
Bioinformatics tool accurately tracks synthetic: DNA Computer scientists show benefits of bioinformatics with PlasmidHawk February 26th, 2021
![]() Pore-like proteins designed from scratch: By creating barrel-shaped proteins that embed into lipid membranes, biochemist have expanded the bioengineering toolkit February 19th, 2021
Pore-like proteins designed from scratch: By creating barrel-shaped proteins that embed into lipid membranes, biochemist have expanded the bioengineering toolkit February 19th, 2021
![]() A little soap simplifies making 2D nanoflakes: Rice labs experiments refine processing of hexagonal boron nitride January 27th, 2021
A little soap simplifies making 2D nanoflakes: Rice labs experiments refine processing of hexagonal boron nitride January 27th, 2021
Research partnerships
![]() Pore-like proteins designed from scratch: By creating barrel-shaped proteins that embed into lipid membranes, biochemist have expanded the bioengineering toolkit February 19th, 2021
Pore-like proteins designed from scratch: By creating barrel-shaped proteins that embed into lipid membranes, biochemist have expanded the bioengineering toolkit February 19th, 2021