Home > Press > Scientists develop promising vaccine method against recurrent UTI
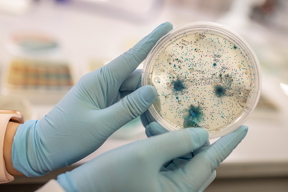 |
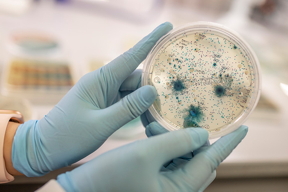
| Dr. Nicole De Nisco conducts research aimed at understanding the basis for recurring urinary tract infections in postmenopausal women. In her lab, students monitor the growth of various bacteria.
Credit:The University of Texas at Dallas |
Abstract:
Researchers at The University of Texas at Dallas are investigating the use of whole-cell vaccines to fight urinary tract infection (UTI), part of an effort to tackle the increasingly serious issue of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Scientists develop promising vaccine method against recurrent UTI
Dallas, TX | Posted on November 19th, 2021
Dr. Nicole De Nisco, assistant professor of biological sciences, and Dr. Jeremiah Gassensmith, associate professor of chemistry and biochemistry, recently demonstrated the use of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) to encapsulate and inactivate whole bacterial cells to create a depot that allows the vaccines to last longer in the body.
The resulting study, published online Sept. 21 in the American Chemical Societys journal ACS Nano, showed that in mice this method produced substantially enhanced antibody production and significantly higher survival rates compared to standard whole-cell vaccine preparation methods.
Vaccination as a therapeutic route for recurrent UTIs is being explored because antibiotics arent working anymore, De Nisco said. Patients are losing their bladders to save their lives because the bacteria cannot be killed by antibiotics or because of an extreme allergy to antibiotics, which is more common in the older population than people may realize.
The American Urological Association estimates that 150 million UTIs occur yearly worldwide, accounting for $6 billion in medical expenditures. If not successfully treated, a UTI can lead to sepsis, which can be fatal.
Recurrent UTI, De Nisco said, is primarily regarded as a womens health issue, and although its common especially in postmenopausal women its something many women dont talk about a lot.
Every subsequent infection becomes more difficult to treat, De Nisco said. Even if you clear the bacteria from the bladder, populations persist elsewhere and usually become resistant to the antibiotic used. When patients accumulate antibiotic resistances, theyre eventually going to run out of options.
De Niscos continuing exploration of how UTIs progress and recur in older women is funded by a recent five-year, $1.3 million grant (R01DK131267) from the National Institutes of Health.
De Niscos collaboration with Gassensmith began in late 2018 after she gave a presentation on the microbiology of UTI to a campus safety protocol committee.
Afterward, we talked about my research groups idea of creating better whole-cell vaccines by preserving antigens in this slow-release depot, Gassensmith said. At the time, we had no real models to test it with, and I thought UTI presented a very good opportunity.
Vaccines work by introducing a small amount of killed or weakened disease-causing germs, or some of their components, to the body. These antigens prompt the immune system to produce antibodies against a particular disease. Building vaccines against pathogenic bacteria is inherently difficult because bacteria are significantly larger and more complex than viruses. Selecting which biological components to use to create antigens has been a major challenge.
Consequently, using the entire cell is preferable to choosing just a piece of a bacterium, Gassensmith said.
We throw the whole kitchen sink at them because thats what your body normally sees when it becomes infected, he said.
The whole-cell approach has its own issues, however.
Vaccines using whole-cell dead bacteria havent succeeded because the cells typically dont last long enough in the body to produce long-term, durable immune responses, Gassensmith said. Thats the reason for our MOF antigen depot: It allows an intact, dead pathogen to exist in tissue longer, as if it were an infection, in order to trigger a full-scale immune system response.
The metal-organic framework Gassensmiths team developed encapsulates and immobilizes an individual bacterium cell in a crystalline polymeric matrix that not only kills the bacterium but also preserves and stabilizes the dead cell against high temperature, moisture and organic solvents.
In their experiments, the researchers used a strain of Escherichia coli. There are no vaccines against any pathogenic strain of this bacterium. Uropathogenic E. coli causes about 80% of all community-acquired UTIs.
When we challenged these mice with a lethal injection of bacteria, after they were vaccinated, almost all of our animals survived, which is a much better performance than with traditional vaccine approaches, Gassensmith said. This result was repeated multiple times, and were quite impressed with how reliable it is.
Although the method has not yet been tested in humans, De Nisco said it has the potential to help millions of patients.
This study on UTI was a proof of concept that whole-cell vaccines are more effective in this extreme, lethal-sepsis model, De Nisco said. Showing that this works against recurrent UTI would be a significant breakthrough.
Beyond recurrent UTI or urosepsis, researchers believe the antigen depot method could be applied broadly to bacterial infections, including endocarditis and tuberculosis.
Were working on translating this approach to TB, which is a very different organism, but like uropathogenic E. coli, when it enters the tissue, it stays, and it recurs, Gassensmith said. It requires a new way of thinking about how vaccines should work.
Vaccine technology is about two centuries old, and it has evolved amazingly little. We hope our platform can open up using existing, well-studied pathogens to create more directed and engineered immune responses.
The project, involving two departments in the School of Natural Sciences and Mathematics, was initially facilitated by the UT Dallas Office of Research and Innovation through a grant to the two scientists from the Seed Program for Interdisciplinary Research. The initiative encourages cross-disciplinary collaboration among University researchers. The research also was funded in part by grants from the National Science Foundation (DMR-1654405 and DMR-2003534) and The Welch Foundation.
Other UT Dallas authors of the ACS Nano article are lead authors Michael Luzuriaga PhD20, now a research fellow in pediatrics at Harvard Medical School, and chemistry doctoral student Fabian Castro Herbert BS18; Dr. Michael Burton, assistant professor of neuroscience; Candace Benjamin PhD20, now a conjugation scientist at Vaxcyte in California; Sarah Popal BS21, a neuroscience graduate applying to dental schools; molecular and cell biology doctoral students Jashkaran Gadhvi, Sundharamani Venkitapathi and Kavya Veera; and chemistry doctoral students Olivia Brohlin, Ryanne Ehrman, Thomas Howlett BS18, Arezoo Shahrivarkevishahi and Yalini Wijesundara.
Immunologist Dr. Molly Ingersoll of the Institut Pasteur in Paris also contributed.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Stephen Fontenot
University of Texas at Dallas
Office: 972-883-4405
Copyright © The University of Texas at Dallas
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
News and information
![]()
How ultracold, superdense atoms become invisible: A new study confirms that as atoms are chilled and squeezed to extremes, their ability to scatter light is suppressed November 19th, 2021
![]()
New microscopy method offers 3D tracking of 100 single molecules at once November 19th, 2021
![]()
Visualizing temperature transport: An unexpected technique for nanoscale characterization November 19th, 2021
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]()
How ultracold, superdense atoms become invisible: A new study confirms that as atoms are chilled and squeezed to extremes, their ability to scatter light is suppressed November 19th, 2021
![]()
Energizer atoms: JILA researchers find new way to keep atoms excited November 19th, 2021
![]()
‘Dancing molecules’ successfully repair severe spinal cord injuries: After single injection, paralyzed animals regained ability to walk within four weeks November 12th, 2021
Possible Futures
![]()
Developing high-performance MXene electrodes for next-generation powerful battery November 19th, 2021
![]()
Efficient photon upconversion at an organic semiconductor interface November 19th, 2021
Nanomedicine
![]()
‘Dancing molecules’ successfully repair severe spinal cord injuries: After single injection, paralyzed animals regained ability to walk within four weeks November 12th, 2021
![]()
Quantum Physics in Proteins: Artificial intelligence affords unprecedented insights into how biomolecules work November 5th, 2021
Discoveries
![]()
Developing high-performance MXene electrodes for next-generation powerful battery November 19th, 2021
![]()
Efficient photon upconversion at an organic semiconductor interface November 19th, 2021
![]()
New microscopy method offers 3D tracking of 100 single molecules at once November 19th, 2021
Announcements
![]()
Efficient photon upconversion at an organic semiconductor interface November 19th, 2021
![]()
New microscopy method offers 3D tracking of 100 single molecules at once November 19th, 2021
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]()
How ultracold, superdense atoms become invisible: A new study confirms that as atoms are chilled and squeezed to extremes, their ability to scatter light is suppressed November 19th, 2021
![]()
Energizer atoms: JILA researchers find new way to keep atoms excited November 19th, 2021
![]()
Developing high-performance MXene electrodes for next-generation powerful battery November 19th, 2021
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]()
‘Dancing molecules’ successfully repair severe spinal cord injuries: After single injection, paralyzed animals regained ability to walk within four weeks November 12th, 2021
![]()
Quantum Collaboration: Two UCSB scientists receive award to partner with Ciscos new Quantum Research Team November 3rd, 2021
![]()
Nanoscale lattices flow from 3D printer: Rice University engineers create nanostructures of glass and crystal for electronics, photonics October 15th, 2021
Nanobiotechnology
![]()
‘Dancing molecules’ successfully repair severe spinal cord injuries: After single injection, paralyzed animals regained ability to walk within four weeks November 12th, 2021
![]()
Quantum Physics in Proteins: Artificial intelligence affords unprecedented insights into how biomolecules work November 5th, 2021
Research partnerships
![]()
Quantum Collaboration: Two UCSB scientists receive award to partner with Ciscos new Quantum Research Team November 3rd, 2021