| Jan 11, 2023 |
|
|
|
(Nanowerk Spotlight) A blockchain is a type of distributed ledger technology (DLT) that consists of a chain of blocks, each containing a list of transactions. Each block also contains a reference to the previous block, forming a chain. This chain of blocks is stored across a decentralized network of computers, rather than in a single central location.
|
|
One of the key features of a blockchain is its immutability, which means that once a block is added to the chain, the information it contains cannot be altered or deleted. This is achieved through the use of cryptographic techniques, such as hashing and digital signatures.
|
|
Another important feature of blockchains is their decentralization, which means that there is no single entity that controls the network. Instead, the network is maintained by a group of participants, known as nodes. Each node has a copy of the entire blockchain, and new blocks are added to the chain through a consensus mechanism, such as proof-of-work or proof-of-stake.
|
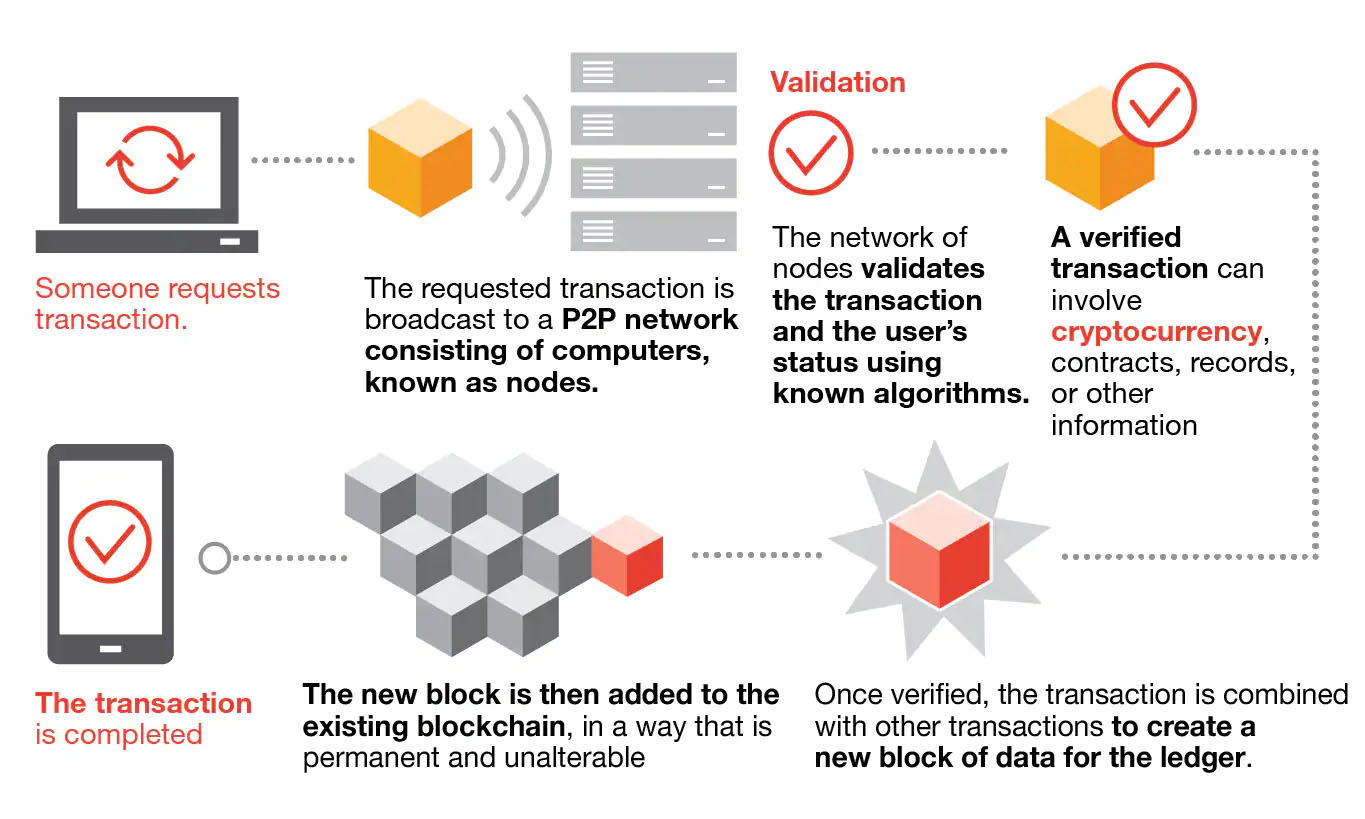 |
| Illustration of blockchain technology. (Source: PwC) (click on image to enlarge)
|
|
One of the most well-known applications of blockchain technology is the cryptocurrency Bitcoin, which uses a blockchain to maintain a decentralized, digital currency. However, the technology has many other potential use cases, such as supply chain management, voting systems, and digital identity verification.
|
|
Blockchain is open source, and it is often used as a public ledger, but private or permissioned blockchain are also used to satisfy certain use cases or industries where data need to be kept private and controlled access.
|
|
Overall, blockchain technology offers a way to securely and transparently store and transfer digital information, without the need for a central authority.
|
|
In the field of science and research, blockchain technology can be used in various ways to improve the transparency, integrity, and security of data. For example, it can be used to create a tamper-evident record of research data, facilitate collaborations between researchers, protect intellectual property, fund scientific projects, and track the movement of materials throughout the supply chain. By using blockchain, researchers can ensure that their work is properly credited and cited, and that the data they collect is accurately recorded and preserved for future use.
|
|
In the following we will look at some examples of how blockchain could used to
|
|
– Make storage of research date safer
– Increase transparency in the lab workflow and output
– Protect intellectual property
– Unlock new funding sources
– Enhance the peer review process
|
Making Data Storage Safer
|
|
Blockchain technology can make storing and sharing research data safer in several ways:
|
|
Decentralized storage: One of the main benefits of blockchain is that it is decentralized, meaning that it is not controlled by a single entity. This makes it more resistant to tampering and data breaches, as there is no single point of failure.
|
|
Cryptographic security: Blockchain uses advanced cryptography to secure the data that is recorded on the blockchain. This makes it difficult for unauthorized parties to access or alter the data.
|
|
Tamper-evident record of research data: Because each block in the blockchain is linked to the previous block, any attempt to alter the data in a block would be immediately detectable. This makes it easier to detect and prevent tampering with the data.
|
|
Data backup and recovery: Blockchain networks typically have multiple copies of the data stored on different computers, making it easier to recover the data in the event of a failure or data loss.
|
|
Overall, the decentralized, secure, and tamper-evident nature of blockchain technology makes it a safer option for storing data compared to traditional centralized storage systems.
|
Transparency in the lab workflow and output
|
|
Day-to-day lab operations rely on properly mapped out workflows to manage people, tasks, and systems so that work follows a consistent process, everybody is clear about their tasks and deadlines, and clear record keeping procedues are followed.
|
 |
| Does the workflow in your lab look like this? (Image: Artel)
|
|
There are several ways in which blockchain technology can make research more transparent:
|
|
Blockchain can be used to improve experimental record keeping by creating a decentralized, tamper-proof record of all the data generated in a lab. Blockchain-based systems can be used to record data from experiments, including the conditions under which the experiment was performed, the results obtained, and the conclusions drawn. This creates a permanent and tamper-proof record of the experiment that can be accessed and verified by other researchers, ensuring the integrity and reproducibility of the research. By using blockchain, researchers can ensure that the data they collect is accurately recorded and preserved for future use.
|
Tracking contributions to research collaborations: Blockchain can be used to track the contributions of different researchers to a project, making it easier to see who has contributed what and to give credit where it is due.
Verifying scientific discoveries: Researchers can use blockchain to create a verifiable record of their scientific discoveries, helping to ensure that their work is properly credited and cited.
|
|
Another way blockchain can be used to improve experimental record keeping is by using smart contracts to automate certain aspects of the lab workflow. For example, a smart contract could be set up to automatically trigger the release of funds for a specific experiment once certain conditions have been met, or to automatically notify the appropriate parties when an experiment is completed.
|
|
Additionally, blockchain can be used to track the provenance of samples, reagents and equipment, ensuring that they are not contaminated or otherwise compromised. This could be done by creating a decentralized system for tracking the movement and storage of these materials and ensuring that they are not tampered with. An example of platform using this approach is Ambrosus, a blockchain-powered IoT platform that allows to track and trace the lifecycle of products, ensuring authenticity, quality and safety.
|
|
Overall, the use of blockchain technology to improve experimental record keeping in research laboratories has the potential to increase transparency, security, and automation in the record keeping process, which may lead to more efficient and reliable research, benefiting the entire scientific community.
|
Protecting intellectual property
|
|
Researchers can use blockchain to create a permanent, unalterable record of their intellectual property, such as patents or copyrighted materials.
|
|
Blockchain technology has the potential to be used as a tool to protect intellectual property rights (IPR) by providing a secure and tamper-proof way to record and manage ownership and rights information for creative works. For instance, the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) is exploring the use of blockchain to create a permanent record of intellectual property rights.
|
|
One way this could be done is through the use of blockchain-based smart contracts. A smart contract is a self-executing contract with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code. These contracts can be programmed to automatically transfer ownership and rights when certain conditions are met. For example, a smart contract could be set up to automatically transfer ownership of a piece of artwork to a collector when payment is received, and to automatically distribute royalties to the artist whenever the work is resold.
|
|
Another way blockchain can be used to protect intellectual property is by using it as a tool for managing and tracking the distribution of digital assets such as music, videos, and software. For example, the platform Po.et uses blockchain technology to create a decentralized, digital ledger for managing and tracking the ownership of creative works, including written content, photographs, and videos. By recording the ownership of these works on the blockchain, it becomes much more difficult for someone to claim ownership of a work that they did not create.
|
 |
| Overview of blockchain use in IP ecosystems. (Source: WIPO) (click on image to enlarge)
|
|
The platform of VeChain uses blockchain as well to create a traceability for products in the supply chain, it also uses RFID tags or QR codes to link the physical product to the digital representation on blockchain. This way it helps reducing the cases of counterfeit products and IP infringement.
|
|
One major example of a company which uses the blockchain technology to protect intellectual property is Kodak, which is planning to develop the KodakOne platform. It uses blockchain to create a digital ledger of rights ownership for photographs. This allows photographers to register their work on the platform and receive payment whenever that work is licensed or used by someone else.
|
|
The startup IPwe is using blockchain to create a global database of patents and facilitate the licensing of patented technologies.
|
|
Overall, the potential for blockchain technology to help protect intellectual property rights is significant. These examples and initiatives, show the potential and interest of the industry in using the blockchain technology for protecting IPR and digital assets.
|
Funding scientific research projects
|
|
Blockchain-based platforms in Web3 could be used to fund scientific research projects by allowing individuals and organizations to directly contribute to specific projects. Traditional science funding models direct the flow of capital directly to individual researchers or research groups, while other sources of capital are yet to be tapped. To address this challenge, the decentralized science movement (DeSci) seeks to use blockchain technology to unlock new scientific funding sources and decentralize ownership of the scientific process.
|
|
Blockchain-based platforms have the potential to revolutionize the way scientific research projects are funded by creating new and more efficient ways for researchers and scientists to connect with funding sources and collaborators. Capabilities provided by the technology include:
|
|
Transparency: Data stored on the blockchain is available to all approved participants, creating a single source of truth.
Trust: Data is linked among tamper-proof blocks and is distributed across multiple participants, enabling trust between participants who don’t need to know one another.
Disintermediation: By creating an ecosystem of trust, the blockchain can fulfill the roles of existing intermediaries.
Auditability: Data on the blockchain is everlasting and difficult to change, creating an extensive audit trail.
Smart contracts: Digitally encoded contracts / rules that autonomously and consistently execute on the blockchain provide new methods to agree to terms and validate transaction requirements.
|
|
One way blockchain can be used to fund scientific research is through the use of initial coin offerings (ICOs) or token sales. These are fundraising mechanisms in which a new cryptocurrency is created and sold to investors in exchange for funding. The funds raised through an ICO can be used to support research projects, pay for equipment and personnel, and cover other expenses. A well-known example of a blockchain-based platform that uses this approach is the Gnosis platform which raised $12.5 million in just 15 minutes in 2017 for prediction market application.
|
|
Another way blockchain can be used to fund scientific research is through crowdfunding. Blockchain-based platforms like Kickstarter and GoFundMe can enable researchers to raise money for their projects from a large number of individual donors. For example, the platform Experiment.com uses blockchain technology to provide a decentralized and transparent platform for scientific research crowdfunding and, in which individuals can directly support research projects by contributing funds.
|
|
Blockchain technology can also be used to create decentralized, autonomous organizations (DAOs) which are run by a group of participants rather than a single entity. These DAOs can be used to fund scientific research projects by pooling resources and collectively making decisions about how the funds are spent. For example, the platform Science DAO is a decentralized organization that aims to fund and manage scientific research projects.
|
|
Additionally, blockchain-based platforms can be used to create and manage tokens that represent ownership in a research project, these tokens can be bought, sold, and traded on a blockchain-based marketplace, creating new opportunities for researchers to raise funds and for investors to gain exposure to promising projects.
|
|
Overall, blockchain technology has the potential to create new and more efficient ways for scientific research projects to be funded, by providing new funding mechanisms, and creating more transparent and direct ways for researchers to connect with funding sources and collaborators.
|
Enhancing the peer review process
|
|
Blockchain technology has the potential to enhance the peer review process in scientific publishing by providing a secure and transparent way to record and manage the review process and by creating new opportunities for decentralization and collaboration.
|
|
One way blockchain can be used to enhance the peer review process is by using it to create a tamper-proof and transparent record of the review process. Blockchain-based systems can be used to record the identities of the reviewers, the comments they provide, and the final decision made by the editorial board. This creates a permanent and tamper-proof record of the review process, which can be used to increase transparency and ensure that the process is fair and unbiased. For example, the platform Review.Network uses blockchain technology to create a decentralized platform for scientific peer review.
|
|
Another way blockchain can be used to enhance the peer review process is by using it to create new opportunities for collaboration and decentralization. Blockchain-based platforms can be used to create decentralized, autonomous organizations (DAOs) that are run by a group of participants, rather than a single entity. These DAOs can be used to manage the peer review process, with decisions about which papers to publish being made collectively by the community of reviewers.
|
|
Additionally, blockchain can be used to create a decentralized system for managing the publication and distribution of scientific papers. This can be done by creating a system in which papers are published directly on the blockchain, rather than on centralized platforms like journals, and allowing for a direct transfer of ownership and rights for the papers. For example, the platform Orvium is an open-source blockchain-based platform for managing the entire lifecycle of scholarly publications.
|
|
Overall, the use of blockchain technology to enhance the peer review process in scientific publishing has the potential to increase transparency, security, and collaboration in the process, which may lead to more efficient and fair process of scientific papers review, which benefits the entire scientific community.
|
Blockchain for scientists in a wider context of the Internet of Things (IoT)
|
|
The Internet of Things (IoT) has the potential to revolutionize scientific research with automation, remote monitoring and real-time analysis, reducing costs and improving efficiency:
|
|
Data collection: IoT devices can be used to collect large amounts of data from various sources, such as sensors or other connected devices. This can enable scientists to gather data in real-time, which can be useful in fields such as environmental monitoring or medical research. Since IoT devices often rely on sensitive communication, blockchain technology can be used to secure the communication between these devices. Furthermore, blockchain can be used to store and share the data generated by IoT devices in a secure and decentralized manner, providing a tamper-proof record of the data.
|
|
Automation: IoT devices can automate processes such as data collection, analysis, and storage, which can save scientists time and resources.
|
|
Remote monitoring: IoT devices can be used to remotely monitor experiments, equipment, or other processes, which can enable scientists to conduct research in remote locations or in hazardous environments. This enables scientists to analyze sensor data in real-time, discovering patterns and insights that would otherwise be missed. In this context, IoT devices can use blockchain-based digital identity and access management solutions to control access to their resources, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
|
|
Connectivity: IoT devices can be used to connect scientists with each other, as well as with other data sources and systems, which can facilitate collaboration and information sharing. IoT networks can use blockchain technology to create decentralized networks, in which devices can communicate directly with one another and make decisions independently, reducing the need for a central authority.
|
Potential problems with using blockchain in science and research
|
|
Like any technology, there are potential problems and challenges associated with the use of blockchain in science and research. Some of these include:
|
|
Complexity: Blockchain technology can be complex, and researchers may need to invest time and resources in order to understand how it works and how to use it effectively.
|
|
Integration with existing systems: It may be difficult to integrate blockchain technology with existing systems and processes, which could be a barrier to adoption.
|
|
Scalability: Some blockchain systems may not be able to handle large amounts of data or a large number of transactions, which could limit their usefulness in scientific research.
|
|
Regulation: There may be regulatory hurdles to overcome in order to use blockchain in scientific research, depending on the jurisdiction and the specific use case.
|
|
Cybersecurity risks: As with any digital system, blockchain technology is vulnerable to cybersecurity attacks, which could compromise the security and integrity of the data stored on the blockchain.
|
|
Overall, while the use of blockchain in science and research has the potential to bring many benefits, it is important to carefully consider these potential problems and challenges in order to ensure that the technology is used effectively and safely.
|
Conclusion
|
|
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize the way that science and research are conducted. By using blockchain, researchers can securely store and share data, manage research collaborations, protect intellectual property, fund research projects, improve supply chain transparency, and enhance the peer review process. In addition, blockchain can be used to create a secure, decentralized record of clinical trial data, track environmental data, protect endangered species, and verify scientific discoveries. While there are challenges and potential problems to be addressed, the use of blockchain in science and research has the potential to bring many benefits and improve the transparency, integrity, and security of data.
|
By
Michael
Berger
–
Michael is author of three books by the Royal Society of Chemistry:
Nano-Society: Pushing the Boundaries of Technology,
Nanotechnology: The Future is Tiny, and
Nanoengineering: The Skills and Tools Making Technology Invisible
Copyright ©
Nanowerk
|
|
|




