Home > Press > Danish quantum physicists make nanoscopic advance of colossal significance
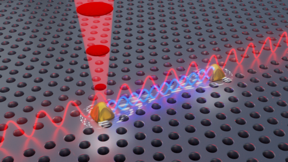 |
| Illustration of two a chip comprising two entangled quantum light sources
CREDIT Peter Lodahl |
Abstract:
In a new breakthrough, researchers at the University of Copenhagen, in collaboration with Ruhr University Bochum, have solved a problem that has caused quantum researchers headaches for years. The researchers can now control two quantum light sources rather than one. Trivial as it may seem to those uninitiated in quantum, this colossal breakthrough allows researchers to create a phenomenon known as quantum mechanical entanglement. This in turn, opens new doors for companies and others to exploit the technology commercially.
Danish quantum physicists make nanoscopic advance of colossal significance
Copenhagen, Denmark | Posted on January 27th, 2023
Going from one to two is a minor feat in most contexts. But in the world of quantum physics, doing so is crucial. For years, researchers around the world have strived to develop stable quantum light sources and achieve the phenomenon known as quantum mechanical entanglement a phenomenon, with nearly sci-fi-like properties, where two light sources can affect each other instantly and potentially across large geographic distances. Entanglement is the very basis of quantum networks and central to the development of an efficient quantum computer.
Today, researchers from the Niels Bohr Institute published a new result in the highly esteemed journal Science, in which they succeeded in doing just that. According to Professor Peter Lodahl, one of the researchers behind the result, it is a crucial step in the effort to take the development of quantum technology to the next level and to “quantize” societys computers, encryption and the internet.
“We can now control two quantum light sources and connect them to each other. It might not sound like much, but its a major advancement and builds upon the past 20 years of work. By doing so, weve revealed the key to scaling up the technology, which is crucial for the most ground-breaking of quantum hardware applications,” says Professor Peter Lodahl, who has conducted research the area since 2001.
The magic all happens in a so-called nanochip which is not much larger than the diameter of a human hair that the researchers also developed in recent years.
Quantum sources overtake the world’s most powerful computer
Peter Lodahl’s group is working with a type of quantum technology that uses light particles, called photons, as micro transporters to move quantum information about.
While Lodahl’s group is a leader in this discipline of quantum physics, they have only been able to control one light source at a time until now. This is because light sources are extraordinarily sensitive to outside “noise”, making them very difficult to copy. In their new result, the research group succeeded in creating two identical quantum light sources rather than just one.
“Entanglement means that by controlling one light source, you immediately affect the other. This makes it possible to create a whole network of entangled quantum light sources, all of which interact with one another, and which you can get to perform quantum bit operations in the same way as bits in a regular computer, only much more powerfully,” explains postdoc Alexey Tiranov, the articles lead author.
This is because a quantum bit can be both a 1 and 0 at the same time, which results in processing power that is unattainable using today’s computer technology. According to Professor Lodahl, just 100 photons emitted from a single quantum light source will contain more information than the world’s largest supercomputer can process.
By using 20-30 entangled quantum light sources, there is the potential to build a universal error-corrected quantum computer the ultimate “holy grail” for quantum technology, that large IT companies are now pumping many billions into.
Other actors will build upon the research
According to Lodahl, the biggest challenge has been to go from controlling one to two quantum light sources. Among other things, this has made it necessary for researchers to develop extremely quiet nanochips and have precise control over each light source.
With the new research breakthrough, the fundamental quantum physics research is now in place. Now it is time for other actors to take the researchers’ work and use it in their quests to deploy quantum physics in a range of technologies including computers, the internet and encryption.
“It is too expensive for a university to build a setup where we control 15-20 quantum light sources. So, now that we have contributed to understanding the fundamental quantum physics and taken the first step along the way, scaling up further is very much a technological task,” says Professor Lodahl.
The research was conducted at the Danish National Research Foundation’s “Center of Excellence for Hybrid Quantum Networks (Hy-Q)” and is a collaboration between Ruhr University Bochum in Germany and the the University of Copenhagens Niels Bohr Institute.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contact
Michael Jensen
University of Copenhagen – Faculty of Science
Office: 459-356-5897
Expert Contact
Peter Lodahl, professor
Niels Bohr Institute, University og Copenhagen
Cell: + 45 20 56 53 03
Alexey Tiranov
Postdoc
Niels Bohr Institute
University of Copenhagen
Phone: + 45 35 33 51 39
Email:
Copyright © University of Copenhagen – Faculty of Science
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
News and information
![]()
Stability of perovskite solar cells reaches next milestone January 27th, 2023
![]()
Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
![]()
Temperature-sensing building material changes color to save energy January 27th, 2023
Quantum Physics
![]()
Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
Possible Futures
![]()
Stability of perovskite solar cells reaches next milestone January 27th, 2023
![]()
UC Irvine researchers decipher atomic-scale imperfections in lithium-ion batteries: Team used super high-resolution microscopy enhanced by deep machine learning January 27th, 2023
Quantum Computing
![]()
Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
Discoveries
![]()
Stability of perovskite solar cells reaches next milestone January 27th, 2023
![]()
Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
![]()
Temperature-sensing building material changes color to save energy January 27th, 2023
Announcements
![]()
Temperature-sensing building material changes color to save energy January 27th, 2023
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]()
Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
![]()
Temperature-sensing building material changes color to save energy January 27th, 2023
![]()
UC Irvine researchers decipher atomic-scale imperfections in lithium-ion batteries: Team used super high-resolution microscopy enhanced by deep machine learning January 27th, 2023
Quantum nanoscience
![]()
Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023










