Home > Press > Development of new photovoltaic commercialization technology: The cause for efficiency degradation in an actual operating environment has been identified, with proposal of material processing method for improving performance stability
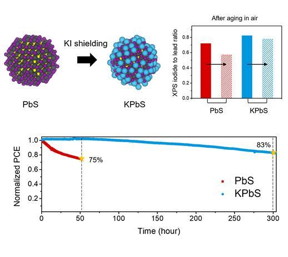 |
| Illustration of stable initial PCE under the actual operating environment of PV devices with the deployment of KI.
CREDIT DGIST |
Abstract:
A technology to further accelerate the commercialization of Colloidal Quantum Dot(CQD) Photovoltaic(PV) devices, which are expected to be next-generation photovoltaic devices, has been developed.
Development of new photovoltaic commercialization technology: The cause for efficiency degradation in an actual operating environment has been identified, with proposal of material processing method for improving performance stability
Daegu, Republic of Korea | Posted on April 10th, 2020
On the 30th (Monday), DGIST announced that a research team of Professor Jongmin Choi from the Department of Energy Science & Engineering and Professor Edward H. Sargent from the University of Toronto has identified the cause of the performance degradation in CQD PV devices and developed a material processing method capable of stabilizing the performance of the devices.
Quantum dots have excellent light absorbance and are capable of absorbing light over a wide range of wavelengths. Hence, they have gained expectation as a key material for the next generation photovoltaic devices. In particular, quantum dots are light, flexible, and involve low processing costs; therefore, they can be replaced by supplementing the drawbacks of silicon solar cells currently in use
In this regard, several studies on photoelectric conversion efficiency (PCE) have been conducted with the aim of improving the performance of CQD PV devices. However, very few studies have focused on improving the stability of these devices, which is necessary for the commercialization process. In particular, few studies have used the CQD PV device at the Maximum Power Point, which is the actual operating environment of PV devices.
For this purpose, the research team investigated the causes of performance degradation by continuously exposing them to illumination and oxygen for long periods of time, similar to the actual operating conditions, in order to improve the stability required for the actual commercialization stage of CQD PV devices. As a result, it was identified that the iodine ions on the surface of the quantum dot solids were removed via oxidation, resulting in the formation of an oxide layer. This oxide layer resulted in the deformation of the quantum dot structure, thereby decreasing the efficiency of the device.
The research team developed a ligand substitution method with potassium(K) to improve the low efficiency of the device. Ligand refers to the ions or molecules that bond to the central atom of a complex similar to a branch. Here, potassium iodide, which prevents the oxidation of iodine, was deployed on the surface of quantum dot solids to undergo a substitution process. As a result of application of the invented method, the device maintained its continuous performance rate of over 80%, which is its initial efficiency rate, for 300 hours. This number is a figure that is higher than premeasured performance thus far.
Professor Jongmin Choi from DGIST said, “The study is to demonstrate that the CQD PV device can operate more stably in the actual operating environment,” and further commented, “The results are expected to further accelerate the commercialization of the CQD PV device. “
The results of this study were published on February 20, in a world-leading, international academic journal Advanced Materials (IF = 25.809). Professor Jongmin Choi from the Energy Science & Engineering Department of DGIST participated in this study as the lead author.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Kwanghoon Choi
82-537-851-135
Copyright © DGIST
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
News and information
![]() Two is better than one: Scientists fit two co-catalysts on one nanosheet for better water purification April 16th, 2020
Two is better than one: Scientists fit two co-catalysts on one nanosheet for better water purification April 16th, 2020
![]() Atomic Force Microscopy Can Help Expand the Tire Industrys Magic Triangle April 15th, 2020
Atomic Force Microscopy Can Help Expand the Tire Industrys Magic Triangle April 15th, 2020
![]() Graphene heterostructures with black phosphorus, arsenic enable new infrared detectors April 13th, 2020
Graphene heterostructures with black phosphorus, arsenic enable new infrared detectors April 13th, 2020
Possible Futures
![]() Two is better than one: Scientists fit two co-catalysts on one nanosheet for better water purification April 16th, 2020
Two is better than one: Scientists fit two co-catalysts on one nanosheet for better water purification April 16th, 2020
![]() Atomic Force Microscopy Can Help Expand the Tire Industrys Magic Triangle April 15th, 2020
Atomic Force Microscopy Can Help Expand the Tire Industrys Magic Triangle April 15th, 2020
![]() Hair surface engineering to be advanced by nano vehicles: This new researched technology can help both drug delivery and hair cosmetics industry April 10th, 2020
Hair surface engineering to be advanced by nano vehicles: This new researched technology can help both drug delivery and hair cosmetics industry April 10th, 2020
Discoveries
![]() Graphene heterostructures with black phosphorus, arsenic enable new infrared detectors April 13th, 2020
Graphene heterostructures with black phosphorus, arsenic enable new infrared detectors April 13th, 2020
![]() A new strategy to create 2D magnetic order April 10th, 2020
A new strategy to create 2D magnetic order April 10th, 2020
![]() Hair surface engineering to be advanced by nano vehicles: This new researched technology can help both drug delivery and hair cosmetics industry April 10th, 2020
Hair surface engineering to be advanced by nano vehicles: This new researched technology can help both drug delivery and hair cosmetics industry April 10th, 2020
Announcements
![]() Two is better than one: Scientists fit two co-catalysts on one nanosheet for better water purification April 16th, 2020
Two is better than one: Scientists fit two co-catalysts on one nanosheet for better water purification April 16th, 2020
![]() Atomic Force Microscopy Can Help Expand the Tire Industrys Magic Triangle April 15th, 2020
Atomic Force Microscopy Can Help Expand the Tire Industrys Magic Triangle April 15th, 2020
![]() Graphene heterostructures with black phosphorus, arsenic enable new infrared detectors April 13th, 2020
Graphene heterostructures with black phosphorus, arsenic enable new infrared detectors April 13th, 2020
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Two is better than one: Scientists fit two co-catalysts on one nanosheet for better water purification April 16th, 2020
Two is better than one: Scientists fit two co-catalysts on one nanosheet for better water purification April 16th, 2020
![]() Graphene heterostructures with black phosphorus, arsenic enable new infrared detectors April 13th, 2020
Graphene heterostructures with black phosphorus, arsenic enable new infrared detectors April 13th, 2020
![]() Future quantum computers may pose threat to today’s most-secure communications April 10th, 2020
Future quantum computers may pose threat to today’s most-secure communications April 10th, 2020
Energy
![]() Graphene nanotubes can increase the number of wind turbines to decrease CO2 emissions March 31st, 2020
Graphene nanotubes can increase the number of wind turbines to decrease CO2 emissions March 31st, 2020
![]() Quantum phenomenon governs organic solar cells: Vibronic coherence contributes to photocurrent generation in organic semiconductor heterojunction diodes March 30th, 2020
Quantum phenomenon governs organic solar cells: Vibronic coherence contributes to photocurrent generation in organic semiconductor heterojunction diodes March 30th, 2020
Quantum Dots/Rods
![]() Visible light and nanoparticle catalysts produce desirable bioactive molecules: Simple photochemical method takes advantage of quantum mechanics October 31st, 2019
Visible light and nanoparticle catalysts produce desirable bioactive molecules: Simple photochemical method takes advantage of quantum mechanics October 31st, 2019
Research partnerships
![]() Two is better than one: Scientists fit two co-catalysts on one nanosheet for better water purification April 16th, 2020
Two is better than one: Scientists fit two co-catalysts on one nanosheet for better water purification April 16th, 2020
![]() Graphene heterostructures with black phosphorus, arsenic enable new infrared detectors April 13th, 2020
Graphene heterostructures with black phosphorus, arsenic enable new infrared detectors April 13th, 2020
![]() A new strategy to create 2D magnetic order April 10th, 2020
A new strategy to create 2D magnetic order April 10th, 2020
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Quantum phenomenon governs organic solar cells: Vibronic coherence contributes to photocurrent generation in organic semiconductor heterojunction diodes March 30th, 2020
Quantum phenomenon governs organic solar cells: Vibronic coherence contributes to photocurrent generation in organic semiconductor heterojunction diodes March 30th, 2020
![]() A consensus statement establishes the protocols to assess and report stability of perovskite photovoltaic devices February 1st, 2020
A consensus statement establishes the protocols to assess and report stability of perovskite photovoltaic devices February 1st, 2020
![]() A consensus statement establishes the protocols to study stability of perovskite photovoltaic devices January 24th, 2020
A consensus statement establishes the protocols to study stability of perovskite photovoltaic devices January 24th, 2020










