Home > Press > Highly sensitive and fast response strain sensor based on evanescently coupled micro/nanofibers
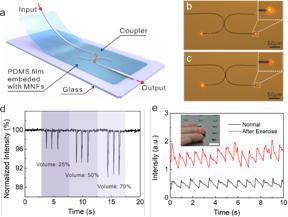 |
| image: Working principle of the strain sensor based on MNF coupler. (a) Schematic diagram of a strain sensor structure. (b), (c) Optical micrographs of an MNF coupler before and after slightly changing of the gap, respectively. The diameter of the MNF is about 900nm, and the bending radius is 50μm. (d) The device response to a metronome at three different volumes. (e) Measurement of the real-time fingertip pulse wave under normal conditions (72 beats per minute) and after exercise (85 beats per minute). The inset shows a photo of the sensor attached to the fingertip to test the pulse of the fingertip, and the scale bar is 1cm.
Credit: OEA |
Abstract:
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances, DOI 10.29026/oea.2022.210101 discusses a highly sensitive and fast response optical strain sensor.
Highly sensitive and fast response strain sensor based on evanescently coupled micro/nanofibers
Chengdu, China | Posted on October 14th, 2022
Strain sensors play an important role in many applications such as flexible electronics , health monitoring, and soft robotics due to their superb response to mechanical deformations. At present, the reported strain sensors mainly focus on high stretchability and high sensitivity under large deformation for motion detection, yet low sensitivity under micro-deformation (≤1%) may limit their applications in micro-displacement detection and weak physiological signal monitoring. Recently, various types of electric strain sensor based on microstructures such as islands structures, percolations and microcracks have been demonstrated for physiological signals detection. However, the complicated processing and high sensitivity to electromagnetic disturbances bring challenges to their practical applications. Alternatively, fiber based optical sensors offer attractive advantages compared with their electronic counterparts, including inherent electrical safety, immunity to electromagnetic interference, and small size. As a combination of fiber optic and nanotechnology, micro/nanofibers (MNFs) have been attracting increasing research interest due to their potential in renewing and expanding fiber optics and flexible sensors in micro/nano scale. Especially, optical coupler based on evanescently coupled MNFs is a promising structure for highly sensitive optical sensing, as the coupling efficiency is strongly dependent on the ambient refractive index, the coupling length and the gap between the two adjacent MNFs. Recently, a highly sensitive and fast response optical strain sensor with two evanescently coupled optical micro/nanofibers (MNFs) embedded in a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) film is proposed. The strain sensor exhibits a gauge factor as high as 64.5 for strain ≤ 0.5% and a strain resolution of 0.0012% which corresponds to elongation of 120 nm on a 1 cm long device. As a proof-of-concept, highly sensitive fingertip pulse measurement is realized. The properties of fast temporal frequancy response up to 30 kHz and a pressure sensitivity of 102 kPa-1 enable the sensor for sound detection. Such versatile sensor could be of great use in physiological signal monitoring, voice recognition and micro-displacement detection.
The authors of this article propose a highly sensitive and fast response optical strain sensor, as shown in Figure 1a. Each U-shaped MNF has a diameter of 0.9 μm and bending radius of 50 μm. As the evanescent field decays exponentially outside the MNFs, the coupling efficiency is very sensitive to the gap between the two MNFs. Thus, any displacement between two MNFs will be reflected upon the change of optical intensity at the output port, thereby realizing highly sensitive strain sensing. The whole structure is embedded in a PDMS film of appropriate thickness to ensure that the strain is transduced to the sensor with high fidelity. The PDMS film can isolate the sensing region from the air, thereby avoiding unpredictable signal interference caused by dust deposition and other external environmental changes. Figure 1b and c shows that such coupler is sensitive to gap widths, as the output intensity changes dramatically when gap width changes slightly. The specially designed MNFs structure and the flexibility of PDMS endow the sensor with high sensitivity and good ductility. The sensor achieved a gauge factor of 64.5 in the range of 0-0.1% strain, and a fast temporal frequency response up to 30 kHz for sound detection. The sensor can also perform sound vibrations detection (Figure 1d) and real-time monitoring of human fingertip pulse (Figure 1e). In addition, the sensor has properties as simple device structure, low requests for light source and detector. Moreover, taking advantage of wavelength-insensitive device response, halogen tungsten lamp and spectrometer used in the experiments can be replaced by cost-effective devices, such as an LED and photodiode, respectively, which is favorable for wearable weak physiological signal sensing system. The proposed new sensor would open a simple route to low-cost, sensitive multifunctional flexible sensors with great potential in medical
Prof. Tongs group is in the College of Optical Science and Engineering, and the State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentation at Zhejiang University. The group explores the science, technology and art of light on the nanoscale. Their research interests include calculation, fabrication, manipulation, characterization and functionalization of low-dimensional photonic structures for both scientific research and technological applications.
Wei Fang is currently an Associate Professor at College of Optical Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University. His current research interests include micro/nanofiber fabrication and application, quantum optics and nonlinear optics. He has published more than 80 academic papers and more than 3000 SCI citations. He has made 10 invited reports at international and domestic academic conferences and obtained 4 national invention patents.
Lei Zhang is currently a Professor at College of Optical Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University. He has joined Zhejiang Lab as a Principal Investigator. His current research interests include flexible micro-nano fiber sensors, humanoid tactile sensors and optical fluidic micro-nano fiber sensors. He has published more than 50 papers in major international journals such as Nature Communications, Advanced Materials, Nano Letters, etc.
Limin Tong is a professor at the School of Optoelectronic Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University. His research interests include the theoretical basis, functional structure and device applications of micro-nano photonics. He is the winner of National Science Fund for Outstanding Young Scholars, Chang Jiang Distinguished Professor of the Ministry of Education, OSA Fellow of the Optical Society of America. He has more than 10 research achievements been reported or reviewed by Science, Nature, Nature Nanotechnology, Nature Materials, etc. He has published two academic monographs (edited) and more than 200 academic papers in Nature, Science, etc. He has been cited for more than 10,000 times.
####
About Compuscript Ltd
Opto-Electronic Advances (OEA) is a high-impact, open access, peer reviewed monthly SCI journal with an impact factor of 8.933 (Journal Citation Reports for IF2021). Since its launch in March 2018, OEA has been indexed in SCI, EI, DOAJ, Scopus, CA and ICI databases over the time and expanded its Editorial Board to 36 members from 17 countries and regions (average h-index 49).
The journal is published by The Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, aiming at providing a platform for researchers, academicians, professionals, practitioners, and students to impart and share knowledge in the form of high quality empirical and theoretical research papers covering the topics of optics, photonics and optoelectronics.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Conor Lovett
Compuscript Ltd
Office: 353-614-75205
Copyright © Compuscript Ltd
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
News and information
![]()
Changing direction: Research team discovers switchable electronic chirality in an achiral Kagome superconductor October 14th, 2022
![]()
Physicists from the University of Warsaw and the Military University of Technology have developed a new photonic system with electrically tuned topological features October 14th, 2022
![]()
Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
Possible Futures
![]()
Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
![]()
New measurements quantifying qudits provide glimpse of quantum future October 14th, 2022
Sensors
![]()
Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
![]()
Silicon image sensor that computes: Device speeds up, simplifies image processing for autonomous vehicles and other applications August 26th, 2022
Discoveries
![]()
Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
Announcements
![]()
New measurements quantifying qudits provide glimpse of quantum future October 14th, 2022
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]()
New measurements quantifying qudits provide glimpse of quantum future October 14th, 2022










