Home > Press > How surface roughness influences the adhesion of soft materials: Research team discovers universal mechanism that leads to adhesion hysteresis in soft materials
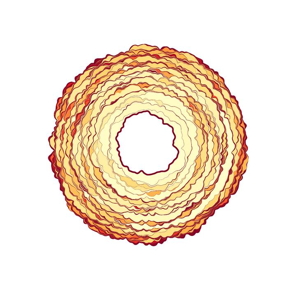 |
| The simulation shows the contact area of a soft solid that is separated from a rough surface. Each coloured spot corresponds to an instability of the contact. The different colour intensity shows how much energy is lost in the process.
CREDIT Antoine Sanner, Lars Pastewka. |
Abstract:
Adhesive tape or sticky notes are easy to attach to a surface, but are difficult to remove. This phenomenon, known as adhesion hysteresis, can be fundamentally observed in soft, elastic materials: Adhesive contact is formed more easily than it is broken. Researchers at the University of Freiburg, the University of Pittsburgh and the University of Akron in the US have now discovered that this adhesion hysteresis is caused by the surface roughness of the adherent soft materials. Through a combination of experimental observations and simulations, the team demonstrated that roughness interferes with the separation process, causing the materials to detach in minute, abrupt movements, which release parts of the adhesive bond incrementally. Dr. Antoine Sanner and Prof. Dr. Lars Pastewka from the Department of Microsystems Engineering and the livMatS Cluster of Excellence at the University of Freiburg, Dr. Nityanshu Kumar and Prof. Dr. Ali Dhinojwala from the University of Akron and Prof. Dr. Tevis Jacobs from the University of Pittsburgh have published their results in the prestigious journal Science Advances.
How surface roughness influences the adhesion of soft materials: Research team discovers universal mechanism that leads to adhesion hysteresis in soft materials
Freiburg, Germany | Posted on March 8th, 2024
Our findings will make it possible to specifically control the adhesion properties of soft materials through surface roughness, says Sanner. They will also allow new and improved applications to be developed in soft robotics or production technology in the future, for example for grippers or placement systems.
Sudden jumping movement of the edge of the contact
Until now, researchers have hypothesized that viscoelastic energy dissipation causes adhesion hysteresis in soft solids. In other words, energy is lost to heat in the material because it deforms in the contact cycle: It is compressed when making contact and expands during release. Those energy losses counteract the movement of the contact surface, which increases the adhesive force during separation. Contact ageing, i.e. the formation of chemical bonds on the contact surface, has also been suggested as a cause. Here the longer the contact exists, the greater the adhesion. Our simulations show that the observed hysteresis can be explained without these specific energy dissipation mechanisms. The only source of energy dissipation in our numerical model is the sudden jumping movement of the edge of the contact, which is induced by the roughness, says Sanner.
Adhesion hysteresis calculated for realistic surface roughness
This sudden jumping motion is clearly recognisable in the simulations of the Freiburg researchers and in the adhesion experiments of the University of Akron. The abrupt change in the contact surface was already mentioned in the 1990s as a possible cause of adhesion hysteresis, but previous theoretical work on this was limited to simplified surface properties,” explains Kumar. We have succeeded for the first time in calculating the adhesion hysteresis for realistic surface roughness. This is based on the efficiency of the numerical model and an extremely detailed surface characterisation carried out by researchers at the University of Pittsburgh, says Jacobs.
About the Cluster of Excellence livMatS
The vision of the Cluster of Excellence Living, Adaptive, and Energy-Autonomous Materials Systems (livMatS) is to combine the best of both worlds nature and technology. livMatS develops lifelike materials systems inspired by nature. These systems adapt autonomously to their environment, harvest clean energy from their surroundings, and are insensitive to or able to recover from damage.
Prof. Dr. Lars Pastewka has been Professor of Simulation at the Faculty of Engineering and a member of the Cluster of Excellence Living, Adaptive and Energy-autonomous Materials Systems (livMatS) at the University of Freiburg since 2017.
Dr. Antoine Sanner completed his doctorate at the Department of Microsystems Engineering and in the Cluster of Excellence livMatS.
The study was funded by the German Research Foundation (livMatS – EXC 2193), the European Research Council (StG 757343), the National Science Foundation (DMR-2208464) and the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (R21 OH012126).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Isabelle Mittermeier
University of Freiburg
Office of University and Science Communications
University of Freiburg
Tel.: 0761/203-4302
e-mail:
Sonja Seidel
Science Communications Cluster of Excellence livMatS
University of Freiburg
Tel.: 0761/203-95361
Copyright © University of Freiburg
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
News and information
![]()
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]()
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Discoveries
![]()
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]()
Researchers approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]()
High-tech ‘paint’ could spare patients repeated surgeries March 8th, 2024
![]()
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]()
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]()
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
![]()
Finding the most heat-resistant substances ever made: UVA Engineering secures DOD MURI award to advance high-temperature materials December 8th, 2023
Announcements
![]()
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]()
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]()
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
![]()
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]()
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]()
Researchers approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]()
‘Sudden death’ of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
![]()
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]()
Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materialspotentially inside the body December 8th, 2023










