Home > Press > Inexpensive, portable detector identifies pathogens in minutes
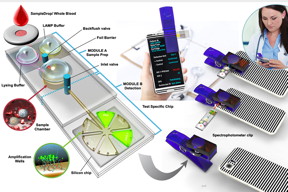 |
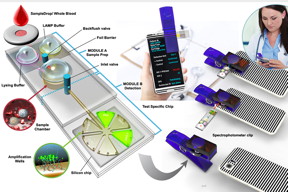
| A schematic drawing of the new device system.
Graphic courtesy Brian Cunningham |
Abstract:
Most viral test kits rely on labor- and time-intensive laboratory preparation and analysis techniques; for example, tests for the novel coronavirus can take days to detect the virus from nasal swabs. Now, researchers have demonstrated an inexpensive yet sensitive smartphone-based testing device for viral and bacterial pathogens that takes about 30 minutes to complete. The roughly $50 smartphone accessory could reduce the pressure on testing laboratories during a pandemic such as COVID-19.
Inexpensive, portable detector identifies pathogens in minutes
Champaign, IL | Posted on April 23rd, 2020
The results of the new multi-institutional study, led by University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign electrical and computer engineering professor Brian Cunningham and bioengineering professor Rashid Bashir, are reported in the journal Lab on a Chip.
“The challenges associated with rapid pathogen testing contribute to a lot of uncertainty regarding which individuals are quarantined and a whole host of other health and economic issues,” Cunningham said.
The study began with the goal of detecting a panel of viral and bacterial pathogens in horses, including those that cause severe respiratory illnesses similar to those presented in COVID-19, the researchers said.
“Horse pathogens can lead to devastating diseases in animal populations, of course, but one reason we work with them has to do with safety. The horse pathogens in our study are harmless to humans,” Cunningham said.
The new testing device is comprised of a small cartridge containing testing reagents and a port to insert a nasal extract or blood sample, the researchers said. The whole unit clips to a smartphone.
Inside the cartridge, the reagents break open a pathogen’s outer shell to gain access to its RNA. A primer molecule then amplifies the genetic material into many millions of copies in about 10 or 15 minutes, the researchers said. A fluorescent dye stains the copies and glows green when illuminated by blue LED light, which is then detected by the smartphone’s camera.
“This test can be performed rapidly on passengers before getting on a flight, on people going to a theme park or before events like a conference or concert,” Cunningham said. “Cloud computing via a smartphone application could allow a negative test result to be registered with event organizers or as part of a boarding pass for a flight. Or, a person in quarantine could give themselves daily tests, register the results with a doctor, and then know when it’s safe to come out and rejoin society.”
There are a few preparatory steps currently performed outside of the device, and the team is working on a cartridge that has all of the reagents needed to be a fully integrated system. Other researchers at the U. of I. are using the novel coronavirus genome to create a mobile test for COVID-19, and making an easily manufactured cartridge that Cunningham said would improve testing efforts.
###
Study co-authors with Cunningham and Bashir were Fu Sun, Anurup Ganguli and Matthew B. Wheeler, of the U. of I.; and Ryan Brisbin and David L. Hirschberg, of RAIN Incubator; Krithika Shanmugam, of the University of Washington; and veterinarian David M. Nash.
The National Science Foundation and the Center for Genomic Diagnostics at the U. of I. ‘s Carl R. Woese Institute for Genomic Biology supported this research.
Bashir also is the dean of the Grainger College of Engineering at Illinois.
Cunningham also is affiliated with bioengineering and materials science and engineering, the Carl R. Woese Institute for Genomic Biology, the Holonyak Micro and Nanotechnology Lab, the Carle Illinois College of Medicine and the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology at Illinois.
Cunningham serves as a consultant to and owns stock in Reliant Immune Diagnostics, the company that licensed the technology described in this news release.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Brian Cunningham, call 217- 265-6291;
Lois Yoksoulian
217-244-2788
@NewsAtIllinois
Copyright © University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
News and information
![]() Fueling the World Sustainably: Synthesizing Ammonia using Less Energy April 26th, 2020
Fueling the World Sustainably: Synthesizing Ammonia using Less Energy April 26th, 2020
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() FSU researchers discover new structure for promising class of materials April 24th, 2020
FSU researchers discover new structure for promising class of materials April 24th, 2020
![]() Argonne scientists fashion new class of X-ray detector: New perovskite-based detectors can sense X-rays over a broad energy range. April 24th, 2020
Argonne scientists fashion new class of X-ray detector: New perovskite-based detectors can sense X-rays over a broad energy range. April 24th, 2020
![]() Multi-functionalization of graphene for molecular targeted cancer therapy April 24th, 2020
Multi-functionalization of graphene for molecular targeted cancer therapy April 24th, 2020
Possible Futures
![]() Fueling the World Sustainably: Synthesizing Ammonia using Less Energy April 26th, 2020
Fueling the World Sustainably: Synthesizing Ammonia using Less Energy April 26th, 2020
![]() Argonne scientists fashion new class of X-ray detector: New perovskite-based detectors can sense X-rays over a broad energy range. April 24th, 2020
Argonne scientists fashion new class of X-ray detector: New perovskite-based detectors can sense X-rays over a broad energy range. April 24th, 2020
Nanomedicine
![]() Multi-functionalization of graphene for molecular targeted cancer therapy April 24th, 2020
Multi-functionalization of graphene for molecular targeted cancer therapy April 24th, 2020
![]() UTEP researchers develop nanohybrid vehicle to optimally deliver drugs into the human body April 23rd, 2020
UTEP researchers develop nanohybrid vehicle to optimally deliver drugs into the human body April 23rd, 2020
![]() Researchers achieve remote control of hormone release April 17th, 2020
Researchers achieve remote control of hormone release April 17th, 2020
![]() Nanoparticles: Acidic alert April 17th, 2020
Nanoparticles: Acidic alert April 17th, 2020
Discoveries
![]() Fueling the World Sustainably: Synthesizing Ammonia using Less Energy April 26th, 2020
Fueling the World Sustainably: Synthesizing Ammonia using Less Energy April 26th, 2020
![]() Multi-functionalization of graphene for molecular targeted cancer therapy April 24th, 2020
Multi-functionalization of graphene for molecular targeted cancer therapy April 24th, 2020
Announcements
![]() Fueling the World Sustainably: Synthesizing Ammonia using Less Energy April 26th, 2020
Fueling the World Sustainably: Synthesizing Ammonia using Less Energy April 26th, 2020
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Fueling the World Sustainably: Synthesizing Ammonia using Less Energy April 26th, 2020
Fueling the World Sustainably: Synthesizing Ammonia using Less Energy April 26th, 2020
![]() Argonne scientists fashion new class of X-ray detector: New perovskite-based detectors can sense X-rays over a broad energy range. April 24th, 2020
Argonne scientists fashion new class of X-ray detector: New perovskite-based detectors can sense X-rays over a broad energy range. April 24th, 2020
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Multi-functionalization of graphene for molecular targeted cancer therapy April 24th, 2020
Multi-functionalization of graphene for molecular targeted cancer therapy April 24th, 2020
![]() Mind over body: The search for stronger brain-computer interfaces April 20th, 2020
Mind over body: The search for stronger brain-computer interfaces April 20th, 2020
![]() Two is better than one: Scientists fit two co-catalysts on one nanosheet for better water purification April 16th, 2020
Two is better than one: Scientists fit two co-catalysts on one nanosheet for better water purification April 16th, 2020
Nanobiotechnology
![]() UTEP researchers develop nanohybrid vehicle to optimally deliver drugs into the human body April 23rd, 2020
UTEP researchers develop nanohybrid vehicle to optimally deliver drugs into the human body April 23rd, 2020
![]() New COVID-19 test quickly and accurately detects viral RNA April 17th, 2020
New COVID-19 test quickly and accurately detects viral RNA April 17th, 2020
![]() Nanoparticles: Acidic alert April 17th, 2020
Nanoparticles: Acidic alert April 17th, 2020