Home > Press > International research team uses wavefunction matching to solve quantum many-body problems: New approach makes calculations with realistic interactions possible
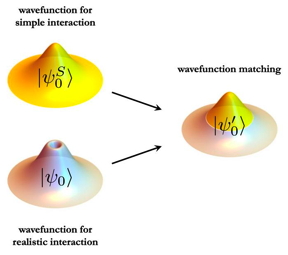 |
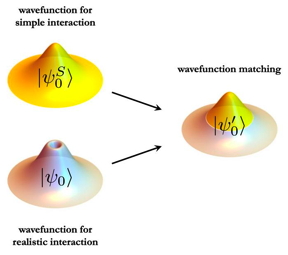
| Wavefunction matching replaces the short distance part of the two-body wavefunction for a realistic interaction with that of a simple easily computable interaction. The result is a new interaction that can be handled in quantum many-body calculations.
CREDIT Figure courtesy of the Facility for Rare Isotope Beams |
Abstract:
FRIB researchers are part of an international research team solving challenging computational problems in quantum physics using a new method called wavefunction matching. The new approach has applications to fields such as nuclear physics, where it is enabling theoretical calculations of atomic nuclei that were previously not possible. The details are published in Nature (Wavefunction matching for solving quantum many-body problems).
International research team uses wavefunction matching to solve quantum many-body problems: New approach makes calculations with realistic interactions possible
East Lansing, MI | Posted on May 17th, 2024
Ab initio methods and their computational challenges
An ab initio method describes a complex system by starting from a description of its elementary components and their interactions. For the case of nuclear physics, the elementary components are protons and neutrons. Some key questions that ab initio calculations can help address are the binding energies and properties of atomic nuclei not yet observed and linking nuclear structure to the underlying interactions among protons and neutrons.
Yet, some ab initio methods struggle to produce reliable calculations for systems with complex interactions. One such method is quantum Monte Carlo simulations. In quantum Monte Carlo simulations, quantities are computed using random or stochastic processes. While quantum Monte Carlo simulations can be efficient and powerful, they have a significant weakness: the sign problem. The sign problem develops when positive and negative weight contributions cancel each other out. This cancellation results in inaccurate final predictions. It is often the case that quantum Monte Carlo simulations can be performed for an approximate or simplified interaction, but the corresponding simulations for realistic interactions produce severe sign problems and are therefore not possible.
Using plastic surgery to make calculations possible
The new wavefunction-matching approach is designed to solve such computational problems. The research teamfrom Gaziantep Islam Science and Technology University in Turkey; University of Bonn, Ruhr University Bochum, and Forschungszentrum Jülich in Germany; Institute for Basic Science in South Korea; South China Normal University, Sun Yat-Sen University, and Graduate School of China Academy of Engineering Physics in China; Tbilisi State University in Georgia; CEA Paris-Saclay and Université Paris-Saclay in France; and Mississippi State University and the Facility for Rare Isotope Beams (FRIB) at Michigan State University (MSU)includes Dean Lee, professor of physics at FRIB and in MSUs Department of Physics and Astronomy and head of the Theoretical Nuclear Science department at FRIB, and Yuan-Zhuo Ma, postdoctoral research associate at FRIB.
We are often faced with the situation that we can perform calculations using a simple approximate interaction, but realistic high-fidelity interactions cause severe computational problems, said Lee. Wavefunction matching solves this problem by doing plastic surgery. It removes the short-distance part of the high-fidelity interaction, and replaces it with the short-distance part of an easily computable interaction.
This transformation is done in a way that preserves all of the important properties of the original realistic interaction. Since the new wavefunctions look similar to that of the easily computable interaction, researchers can now perform calculations using the easily computable interaction and apply a standard procedure for handling small corrections called perturbation theory.
A team effort
The research team applied this new method to lattice quantum Monte Carlo simulations for light nuclei, medium-mass nuclei, neutron matter, and nuclear matter. Using precise ab initio calculations, the results closely matched real-world data on nuclear properties such as size, structure, and binding energies. Calculations that were once impossible due to the sign problem can now be performed using wavefunction matching.
It is a fantastic project and an excellent opportunity to work with the brightest nuclear scientists in FRIB and around the globe, said Ma. As a theorist, I’m also very excited about programming and conducting research on the world’s most powerful exascale supercomputers, such as Frontier, which allows us to implement wavefunction matching to explore the mysteries of nuclear physics.
While the research team focused solely on quantum Monte Carlo simulations, wavefunction matching should be useful for many different ab initio approaches, including both classical and quantum computing calculations. The researchers at FRIB worked with collaborators at institutions in China, France, Germany, South Korea, Turkey, and United States.
The work is the culmination of effort over many years to handle the computational problems associated with realistic high-fidelity nuclear interactions, said Lee. It is very satisfying to see that the computational problems are cleanly resolved with this new approach. We are grateful to all of the collaboration members who contributed to this project, in particular, the lead author, Serdar Elhatisari.
This material is based upon work supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, the U.S. National Science Foundation, the German Research Foundation, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Chinese Academy of Sciences Presidents International Fellowship Initiative, Volkswagen Stiftung, the European Research Council, the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Security Academic Fund, the Rare Isotope Science Project of the Institute for Basic Science, the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Institute for Basic Science, and the Espace de Structure et de réactions Nucléaires Théorique.
Michigan State University operates the Facility for Rare Isotope Beams (FRIB) as a user facility for the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science (DOE-SC), supporting the mission of the DOE-SC Office of Nuclear Physics. Hosting what is designed to be the most powerful heavy-ion accelerator, FRIB enables scientists to make discoveries about the properties of rare isotopes in order to better understand the physics of nuclei, nuclear astrophysics, fundamental interactions, and applications for society, including in medicine, homeland security, and industry.
The U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of todays most pressing challenges. For more information, visit energy.gov/science.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Karen King
Michigan State University Facility for Rare Isotope Beams
Office: 517-908-7262
Copyright © Michigan State University Facility for Rare Isotope Beams
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
News and information
![]()
Gene therapy relieves back pain, repairs damaged disc in mice: Study suggests nanocarriers loaded with DNA could replace opioids May 17th, 2024
![]()
Oscillating paramagnetic Meissner effect and Berezinskii-Kosterlitz-Thouless transition in cuprate superconductor May 17th, 2024
Physics
![]()
Finding quantum order in chaos May 17th, 2024
Quantum Physics
![]()
Finding quantum order in chaos May 17th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]()
Aston University researcher receives £1 million grant to revolutionize miniature optical devices May 17th, 2024
![]()
NRL charters Navys quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]()
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]()
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]()
Advances in priming B cell immunity against HIV pave the way to future HIV vaccines, shows quartet of new studies May 17th, 2024
![]()
Aston University researcher receives £1 million grant to revolutionize miniature optical devices May 17th, 2024
![]()
Gene therapy relieves back pain, repairs damaged disc in mice: Study suggests nanocarriers loaded with DNA could replace opioids May 17th, 2024
![]()
Oscillating paramagnetic Meissner effect and Berezinskii-Kosterlitz-Thouless transition in cuprate superconductor May 17th, 2024
Discoveries
![]()
Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
![]()
Finding quantum order in chaos May 17th, 2024
![]()
Advances in priming B cell immunity against HIV pave the way to future HIV vaccines, shows quartet of new studies May 17th, 2024
Announcements
![]()
Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
![]()
Finding quantum order in chaos May 17th, 2024
![]()
Oscillating paramagnetic Meissner effect and Berezinskii-Kosterlitz-Thouless transition in cuprate superconductor May 17th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]()
Gene therapy relieves back pain, repairs damaged disc in mice: Study suggests nanocarriers loaded with DNA could replace opioids May 17th, 2024
![]()
Oscillating paramagnetic Meissner effect and Berezinskii-Kosterlitz-Thouless transition in cuprate superconductor May 17th, 2024
![]()
What is “time” for quantum particles? Publication by TU Darmstadt researchers in renowned journal “Science Advances” May 17th, 2024