Home > Press > Laser direct writing of Ga2O3/liquid metal-based flexible humidity sensors
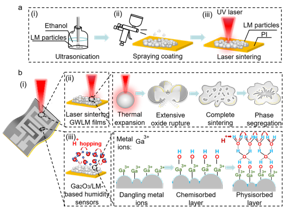 |
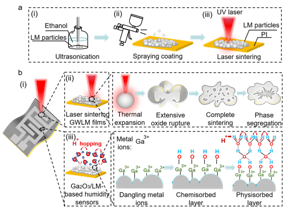
| Design and fabrication of flexible capacitive humidity sensors. (a) Fabrication processes of flexible Ga2O3/LM humidity sensors, including ultrasonication, spraying coating and laser sintering. (b) Schematic of the mechanism to form GWLM films by laser sintering and the sensing mechanism of Ga2O3/LM-based humidity sensors.
CREDIT OEA |
Abstract:
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances, 10.29026/oea.2023.220172 discusses laser direct writing of Ga2O3/liquid metal-based flexible humidity sensors.
Laser direct writing of Ga2O3/liquid metal-based flexible humidity sensors
Sichuan, China | Posted on May 12th, 2023
Recent studies in emerging flexible humidity sensors have achieved great developments in advanced manufacturing methods, as well as innovative applications including human healthcare detection, plant health management and noncontact human-machine interfaces. Capacitive-type humidity sensors have gained much attention due to reliable humidity sensing performance, low power consumption and facile structural designs. Generally, the performance of a capacitive humidity sensor is strongly correlated with the dielectric permittivity of functional materials between sensing electrodes. Until now, various active materials have been investigated as flexible capacitive humidity sensors, such as carbon materials, metal oxides, metal sulfides, and polymers. Similarly, they are typically endowed with large exposed surface areas and rich active sites to interact with water molecules. Ga2O3, as a potential metal oxide with high exposed hydrophilic groups, has been employed as an active material for capacitive humidity sensors. Traditional fabrication techniques to obtain Ga2O3-based humidity sensors mainly involve chemical vapor deposition, thermal treatment, and hydrothermal methods. Nevertheless, these methods usually require high annealing temperature, complicated fabrication procedures as well as various material systems, hindering their practical applications.
Digital laser direct writing is a rapid and environmental-friendly manufacturing approach to generating functional micro/nano-structures or directly creating sensitive nanomaterials with high precision. Based on laser-matter interactions, via judiciously selecting the appropriate laser processing parameters, a variety of innovative flexible sensors, such as physical, chemical and physiological sensors have been demonstrated. The typical strategies usually rely on the laser direct writing of electrodes, followed by the deposition of moisture sensitive nanomaterials, such as carbon or metal sulfides-based materials, on the top of electrodes. However, this leads to multiple complex procedures. Therefore, a facile and simple approach to developing thin film-based humidity sensor is still required.
In this work, a wearable capacitive-type Ga2O3/liquid metal-based humidity sensor is demonstrated by a one-step laser direct writing technique. Owing to the photothermal effect of laser, the Ga2O3-wrapped liquid metal nanoparticles can be selectively sintered and converted from insulative to conductive traces with a resistivity of 0.19 Ω·cm, while the untreated regions serve as active sensing layers in response to moisture changes. Under 95% relative humidity, the humidity sensor displays a highly stable performance along with rapid response and recover time. Utilizing these superior properties, the Ga2O3/liquid metal-based humidity sensor is able to monitor human respiration rate, as well as skin moisture of the palm under different physiological states for healthcare monitoring.
# # # # # #
Prof. Kaichen Xu is a PI of Flexible/Bioelectronic Manufacturing Laboratory, Zhejiang University. He was selected into a National Young Talent Program and received JSPS scholarship. In 2018, he received his PhD degree from the National University of Singapore under the supervision of Professor Hong Minghui (Academician of Singapore Academy of Engineering, now Professor in Xiamen University). Later, he went to Osaka Public University for postdoctoral research with the cooperative supervisor of Professor Kuniharu Takei. In 2020, he joined the School of Mechanical Engineering of Zhejiang University and the team of Academician Huayong Yang. The research group is mainly focused on flexible/bioelectronic manufacturing and laser micro-nano manufacturing. He has published over 30 papers in international journals. He is the editorial board member of Opto-Electronic Engineering, the youth expert of Engineering (Journal of the Chinese Academy of Engineering), and the youth editorial board member of several journals, including Chinese Laser, International Journal of Extreme Manufacturing, Frontiers of Optoelectronics. He is the reviewer for over 40 journals (>180 times). Research homepage: https://blog.nus.edu.sg/xukaichen/
####
About Compuscript Ltd
Opto-Electronic Advances (OEA) is a high-impact, open access, peer reviewed monthly SCI journal with an impact factor of 8.933 (Journal Citation Reports for IF2021). Since its launch in March 2018, OEA has been indexed in SCI, EI, DOAJ, Scopus, CA and ICI databases over the time and expanded its Editorial Board to 36 members from 17 countries and regions (average h-index 49).
The journal is published by The Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, aiming at providing a platform for researchers, academicians, professionals, practitioners, and students to impart and share knowledge in the form of high quality empirical and theoretical research papers covering the topics of optics, photonics and optoelectronics.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Conor Lovett
Compuscript Ltd
Office: 353-614-75205
Copyright © Compuscript Ltd
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
News and information
![]()
Breakthrough in the optical properties of MXenes – two-dimensional heterostructures provide new ideas May 12th, 2023
![]()
Novel design perovskite electrochemical cell for light-emission and light-detection May 12th, 2023
Possible Futures
![]()
Researchers at Purdue discover superconductive images are actually 3D and disorder-driven fractals May 12th, 2023
![]()
Breakthrough in the optical properties of MXenes – two-dimensional heterostructures provide new ideas May 12th, 2023
![]()
Novel design perovskite electrochemical cell for light-emission and light-detection May 12th, 2023
Chip Technology
![]()
Breakthrough in the optical properties of MXenes – two-dimensional heterostructures provide new ideas May 12th, 2023
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]()
Breakthrough in the optical properties of MXenes – two-dimensional heterostructures provide new ideas May 12th, 2023
![]()
Efficient heat dissipation perovskite lasers using a high-thermal-conductivity diamond substrate April 14th, 2023
![]()
Data can now be processed at the speed of light! April 14th, 2023
Sensors
![]()
New family of wheel-like metallic clusters exhibit unique properties April 14th, 2023
![]()
Nanobiotechnology: How Nanomaterials Can Solve Biological and Medical Problems April 14th, 2023
![]()
Diamond cut precision: University of Illinois to develop diamond sensors for neutron experiment and quantum information science April 14th, 2023
Discoveries
![]()
Breakthrough in the optical properties of MXenes – two-dimensional heterostructures provide new ideas May 12th, 2023
![]()
Novel design perovskite electrochemical cell for light-emission and light-detection May 12th, 2023
Announcements
![]()
Breakthrough in the optical properties of MXenes – two-dimensional heterostructures provide new ideas May 12th, 2023
![]()
Novel design perovskite electrochemical cell for light-emission and light-detection May 12th, 2023
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]()
Researchers at Purdue discover superconductive images are actually 3D and disorder-driven fractals May 12th, 2023
![]()
Breakthrough in the optical properties of MXenes – two-dimensional heterostructures provide new ideas May 12th, 2023
![]()
Novel design perovskite electrochemical cell for light-emission and light-detection May 12th, 2023
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]()
Breakthrough in the optical properties of MXenes – two-dimensional heterostructures provide new ideas May 12th, 2023
![]()
Efficient heat dissipation perovskite lasers using a high-thermal-conductivity diamond substrate April 14th, 2023
![]()
Data can now be processed at the speed of light! April 14th, 2023