Home > Press > Modulating MoSe2 functional plane via doping-defect engineering strategy to develop conductive and electrocatalytic mediators in Li-S batteries
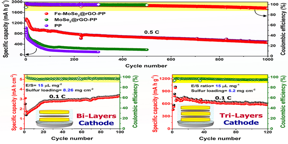 |
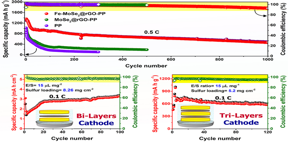
| Fe-MoSe2@rGO provides a promising avenue for producing a developed separator function for practical high-energy-density Li-S batteries. Fe-MoSe2@rGO-PP exhibits excellent cycling stability under lean E/S ratios and high sulfur loading.
CREDIT Journal of Energy Chemistry |
Abstract:
The lithiumsulfur (LiS) battery is considered a promising and efficient energy storage system because of its high energy density (2600 Wh kg-1) and low sulfur material cost. However, numerous obstacles to the practical implementation of LiS batteries remain, including low sulfur conductivity, the shuttle effect, and the requirement for an adequate volume change (80%) of sulfur during charging and discharging operations, which have limited the applicability of LiS batteries.
Modulating MoSe2 functional plane via doping-defect engineering strategy to develop conductive and electrocatalytic mediators in Li-S batteries
Dalian, China | Posted on September 23rd, 2022
Transition metal chalcogenides (TMDs), such as molybdenum diselenide (MoSe2), have received attention as a viable method for accelerating sulfur redox processes. However, the limited number of active sites in MoSe2 considerably reduces their overall electrocatalytic performance. Metal doping into MoSe2 can improve the electronic conductivity of MoSe2 and generate defects, creating numerous reactive sites for catalytic reactions. Moreover, polysulfide transformation in the LiS system can be improved through defect engineering, which can alter the physicochemical and electronic structure to enhance the adsorption and catalytic properties of a material.
Recently, Yutao Dong and Jianmin Zhang (corresponding authors), Mohammed A. Al-Tahan (first author), and others published a manuscript titled Modulating of MoSe2 functional plane via doping-defect engineering strategy for the development of conductive and electrocatalytic mediators in Li-S batteries in the Journal of Energy Chemistry.
The authors demonstrate that introducing iron exposes more active selenium edge sites in MoSe2, which can selectively adsorb more lithium polysulfides (LiPSs) to minimize the shuttle effect. Moreover, the conductive feature of rGO improves the cell’s electrical conductivity and promotes the adsorption of polysulfides via chemical bonding with the functional group of rGO. Therefore, using the nanohybrid as a functional plane offers the advantages of high conductivity and effective LiPS adsorption.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Xiaoluan Wei
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy Sciences
Office: 86-041-184-379-021
Copyright © Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy Sciences
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
News and information
![]()
Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
![]()
Heat-resistant nanophotonic material could help turn heat into electricity: The key to beating the heat is degrading the materials in advance September 23rd, 2022
![]()
Chicago Quantum Exchange welcomes six new partners highlighting quantum technology solutions, from Chicago and beyond September 23rd, 2022
![]()
Twisty photons could turbocharge next-gen quantum communication: Teams on-chip technology uses orbital angular momentum to encode more information into a single photon September 23rd, 2022
Possible Futures
![]()
Chicago Quantum Exchange welcomes six new partners highlighting quantum technology solutions, from Chicago and beyond September 23rd, 2022
![]()
Twisty photons could turbocharge next-gen quantum communication: Teams on-chip technology uses orbital angular momentum to encode more information into a single photon September 23rd, 2022
![]()
Wrapping of nanosize copper cubes can help convert carbon dioxide into other chemicals September 23rd, 2022
![]()
Upgrading your computer to quantum September 23rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]()
Twisty photons could turbocharge next-gen quantum communication: Teams on-chip technology uses orbital angular momentum to encode more information into a single photon September 23rd, 2022
![]()
Upgrading your computer to quantum September 23rd, 2022
![]()
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Announcements
![]()
Heat-resistant nanophotonic material could help turn heat into electricity: The key to beating the heat is degrading the materials in advance September 23rd, 2022
![]()
Chicago Quantum Exchange welcomes six new partners highlighting quantum technology solutions, from Chicago and beyond September 23rd, 2022
![]()
Twisty photons could turbocharge next-gen quantum communication: Teams on-chip technology uses orbital angular momentum to encode more information into a single photon September 23rd, 2022
![]()
Wrapping of nanosize copper cubes can help convert carbon dioxide into other chemicals September 23rd, 2022
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]()
Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
![]()
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]()
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]()
Heat-resistant nanophotonic material could help turn heat into electricity: The key to beating the heat is degrading the materials in advance September 23rd, 2022
![]()
New cathode design solves major barrier to better lithium-ion batteries September 9th, 2022
![]()
Understanding outsize role of nanopores: New research reveals differences in pH, and more, about these previously mysterious environments August 26th, 2022
![]()
Lithiophilic seeds and rigid arrays synergistic induced dendrite-free and stable Li anode towards long-life lithium-oxygen batteries July 22nd, 2022