Home > Press > Nanofibrous metal oxide semiconductor for sensory face
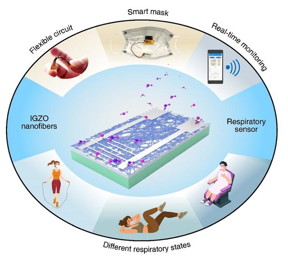 |
| IGZO nanofibre-based sensors are integrated with a flexible circuit to create a sensory face mask, thus featuring wireless and real-time monitoring capabilities.
Credit Qing, M., et al. |
Abstract:
Room-temperature (RT) gas sensors with high sensitivity are essential in low-power Internet-of-Things (IoT) applications, such as smart sensors, wearable devices and mobile robots. Among these, metal oxide semiconductor-based gas sensors are valued for their low production cost, high sensitivity and ease of use, making them suitable for detecting flammable, explosive, toxic, and exhaled gases. However, further fiber diameter reduction and real-time monitoring integration remain underexplored.
Nanofibrous metal oxide semiconductor for sensory face
Beijing, China | Posted on November 8th, 2024
In a study published in the KeAi journal Wearable Electronics, a group of researchers from China and South Korea described a new sensor they have developed ultrathin (~88 nm) amorphous indium gallium zinc oxide (IGZO) nanofibres for wireless and real-time human breath monitoring.
“IGZO nanofibres were created as the charge transport layer to enhance the surface area for gas diffusion using an electrospinning approach, explains the study’s lead author, Qing Ma, a post-doctoral fellow at the School of Electronic Science and Engineering at Southeast University. The resulting field-effect properties demonstrated an average mobility of 2.2 cm²/V·s and an on/off ratio of 10⁵.
Notably, the team successfully recorded human breath in fast, normal and deep states, showing the sensors fast response and recovery times and stable operation. By integrating the sensor with a flexible circuit board and mounting them on a face mask, we achieved wireless and real-time monitoring of respiratory status, highlighting its potential for practical applications in health monitoring, says Ma.
The researchers also found that electrical transport in IGZO nanofibres is driven by oxygen vacancies, water vapor and temperature significantly affect its conductivity. When a voltage is applied, the sensors current significantly decreases and quickly recovers during a breath cycle, with a fast response and recovery time of approximately 0.7 seconds.
According to senior and co-corresponding author Binghao Wang, this is a promising solution in the field of personalised healthcare and pandemic prevention.
An IGZO NF-based sensor integrated into a flexible circuit achieved a compact size of 15 × 35 mm², marking significant progress in the miniaturisation efforts for smart mask technology, says Wang. The recorded electrical signals can be visualised via a smartphone equipped with a customised mobile app, underscoring the potential for the widespread adoption of IGZO TFT-based sensors in wearable technology.”
####
About KeAi Communications Co., Ltd.
The publisher KeAi was established by Elsevier and China Science Publishing & Media Ltd to unfold quality research globally. In 2013, our focus shifted to open access publishing. We now proudly publish more than 100 world-class, open access, English language journals, spanning all scientific disciplines. Many of these are titles we publish in partnership with prestigious societies and academic institutions, such as the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC).
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Ye He
KeAi Communications Co., Ltd.
Office: 521-098-1577
Contact the author: Binghao Wang, School of Electronic Science and Engineering, Southeast University, No. 2 Southeast University Road, Jiangning, Nanjing, Jiangsu 211189, China.
Haoyang Wang, School of Electronic Science and Engineering, Southeast University, No. 2 Southeast University Road, Jiangning, Nanjing, Jiangsu 211189, China.
Copyright © KeAi Communications Co., Ltd.
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
Wearable electronics
![]()
Beyond wires: Bubble technology powers next-generation electronics:New laser-based bubble printing technique creates ultra-flexible liquid metal circuits November 8th, 2024
![]()
CityU awarded invention: Soft, ultrathin photonic material cools down wearable electronic devices June 30th, 2023
News and information
![]()
Beyond wires: Bubble technology powers next-generation electronics:New laser-based bubble printing technique creates ultra-flexible liquid metal circuits November 8th, 2024
![]()
Nanoparticle bursts over the Amazon rainforest: Rainfall induces bursts of natural nanoparticles that can form clouds and further precipitation over the Amazon rainforest November 8th, 2024
![]()
Nanotechnology: Flexible biosensors with modular design November 8th, 2024
![]()
Exosomes: A potential biomarker and therapeutic target in diabetic cardiomyopathy November 8th, 2024
Robotics
![]()
Femtosecond laser technique births “dancing microrobots”: USTC’s breakthrough in multi-material microfabrication August 11th, 2023
Internet-of-Things
![]()
New nanowire sensors are the next step in the Internet of Things January 6th, 2023
![]()
New chip ramps up AI computing efficiency August 19th, 2022
![]()
Lightening up the nanoscale long-wavelength optoelectronics May 13th, 2022
![]()
Thin-film, high-frequency antenna array offers new flexibility for wireless communications November 5th, 2021
Possible Futures
![]()
Nanotechnology: Flexible biosensors with modular design November 8th, 2024
![]()
Exosomes: A potential biomarker and therapeutic target in diabetic cardiomyopathy November 8th, 2024
![]()
Turning up the signal November 8th, 2024
![]()
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]()
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
![]()
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Sensors
![]()
Beyond wires: Bubble technology powers next-generation electronics:New laser-based bubble printing technique creates ultra-flexible liquid metal circuits November 8th, 2024
![]()
Nanotechnology: Flexible biosensors with modular design November 8th, 2024
![]()
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Discoveries
![]()
Breaking carbonhydrogen bonds to make complex molecules November 8th, 2024
![]()
Exosomes: A potential biomarker and therapeutic target in diabetic cardiomyopathy November 8th, 2024
![]()
Turning up the signal November 8th, 2024
![]()
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
Announcements
![]()
Nanotechnology: Flexible biosensors with modular design November 8th, 2024
![]()
Exosomes: A potential biomarker and therapeutic target in diabetic cardiomyopathy November 8th, 2024
![]()
Turning up the signal November 8th, 2024
![]()
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]()
Beyond wires: Bubble technology powers next-generation electronics:New laser-based bubble printing technique creates ultra-flexible liquid metal circuits November 8th, 2024
![]()
Nanoparticle bursts over the Amazon rainforest: Rainfall induces bursts of natural nanoparticles that can form clouds and further precipitation over the Amazon rainforest November 8th, 2024
![]()
Nanotechnology: Flexible biosensors with modular design November 8th, 2024
![]()
Exosomes: A potential biomarker and therapeutic target in diabetic cardiomyopathy November 8th, 2024










