Home > Press > Night-time radiative warming using the atmosphere
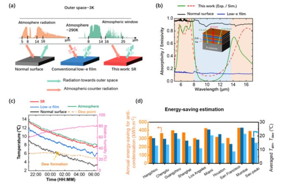 |
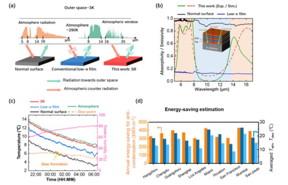
| (a) Schematic diagram of the radiative heat exchange among the atmosphere, the outer space, and the surfaces. (b) Measured absorptivity / emissivity. (c) Real-time temperature in thermal test. (d) Calculated annual energy-saving for anti-condensation of 10 cities in various climate zones.
CREDIT by Yining Zhu, Yiwei Zhou, Bing Qin, Rui Qin, Min Qiu, and Qiang Li |
Abstract:
Warming has played a crucial role in various industrial and agricultural processes throughout history. Night-time warming, however, presents a distinct challenge due to the absence of solar radiation. During the night, direct radiative heat loss to outer space through the atmospheric transparent window (8-14 μm) can cause temperature to drop below freezing, posing significant threats to agriculture (crops), transportation (outdoor cables), and more.
Night-time radiative warming using the atmosphere
Changchun, China | Posted on November 17th, 2023
Traditionally, achieving night-time warming relied on active electric heaters, which contribute to significant energy consumption and increased carbon emissions. Passive warming methods, including insulating blankets (reducing heat conduction) and low-emissivity films (reducing heat radiation), come with limitations, such as suboptimal effectiveness and overall positive net heat loss.
Air, known for its high heat capacity, can maintain relatively higher temperatures compared to the ground during the night, potentially serving as an external heat source. To harness energy from the entire atmosphere above the Earth’s surface, radiative methods are needed.
In a new paper published in Light Science & Application, a team of scientists, led by Professor Qiang Li from Zhejiang University, China, proposed a night-time radiative warming strategy based on nanophotonic control. This strategy passively suppresses the thermal radiation of objects in the atmospheric transparent window (8-14 μm) while actively utilizing energy in the atmospheric radiation bands (5-8 μm and 14-16 μm). Achieving this strategy involves covering the target surface with a selective reflective (SR) thin film that exhibits high reflectance in the atmospheric transparent band and high absorptivity in the atmospheric radiation bands, to control radiative energy flow and effectively raising the target temperature.
Researchers designed and fabricated the device using a broadband infrared-absorbing substrate combined with germanium and zinc sulfide one-dimensional photonic crystal films. The device achieved a reflectance of 0.91 in the atmospheric transparent window and an absorptivity of 0.7 in the atmospheric radiative bands. Then, outdoor thermal testing was conducted, revealing that by covering SR film, the target’s temperature increased by 2.1°C/4.4°C compared to a broadband reflective (low-e) surface and a broadband absorptive surface, respectively.
The study also assessed the potential application of this night-time warming strategy in cities with different climates, demonstrating that the annual electricity savings could surpass 300 kWh m-2 across different climate zones.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contact
Yaobiao Li
Light Publishing Center, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics And Physics, CAS
Office: 86-431-861-76851
Expert Contact
Qiang Li
Zhejiang University, China
Copyright © Light Publishing Center, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics And Physics, CAS
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
News and information
![]()
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]()
A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
Possible Futures
![]()
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]()
Silver nanoparticles: guaranteeing antimicrobial safe-tea November 17th, 2023
![]()
Three-pronged approach discerns qualities of quantum spin liquids November 17th, 2023
![]()
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Discoveries
![]()
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]()
A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
Announcements
![]()
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]()
A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]()
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]()
A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
Food/Agriculture/Supplements
![]()
Silver nanoparticles: guaranteeing antimicrobial safe-tea November 17th, 2023
![]()
DGIST and New Life Group launched a research project on “Functional beauty and health products using the latest nanotechnology” May 12th, 2023
![]()
Manufacturing advances bring material back in vogue January 20th, 2023
![]()
Scientists offer solutions for risky tap water June 17th, 2022
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]()
Light guide plate based on perovskite nanocomposites November 3rd, 2023
![]()
Super-efficient laser light-induced detection of cancer cell-derived nanoparticles: Skipping ultracentrifugation, detection time reduced from hours to minutes! October 6th, 2023