Home > Press > Removing the lead hazard from perovskite solar cells
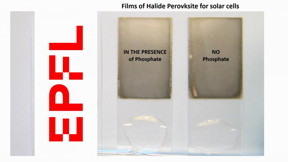 |
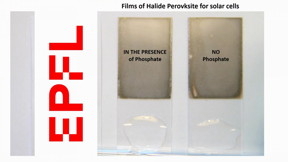
| A transparent phosphate crystal, which incorporated into solar cells, can instantaneously immobilize the lead in case of failure and block its leaching out from the device.
CREDIT Endre Horvth (EPFL) |
Abstract:
“The solar energy-to-electricity conversion of perovskite solar cells is unbelievably high, around 25%, which is now approaching the performance of the best silicon solar cells,” says Professor Lszl Forr at EPFL’s School of Basic Sciences. “But their central element is lead, which is a poison; if the solar panel fails, it can wash out into the soil, get into the food chain, and cause serious diseases.”
Removing the lead hazard from perovskite solar cells
Lausanne, Switzerland | Posted on July 16th, 2021
The problem is that in most of the halide perovskites lead can dissolve in water. This water solubility and solubility in other solvents is actually a great advantage, as it makes building perovskite solar panels simpler and inexpensive – another perk along with their performance. But the water solubility of lead can become a real environmental and health hazard when the panel breaks or gets wet, e.g. when it rains.
So the lead must be captured before it gets to the soil, and it must be possible to recycle it. This issue has drawn much and intensive research because it is the main obstacle for regulatory authorities approving the production of perovskite solar cells on a large, commercial scale. However, attempts to synthesize non-water-soluble and lead-free perovskites have yielded poor performance.
Now, Forr’s group has come up with an elegant and efficient solution, which involves using a transparent phosphate salt, which does not block solar light, so it doesn’t affect performance. And if the solar panel fails, the phosphate salt immediately reacts with lead to produce a water-insoluble compound that cannot leach out to the soil, and which can be recycled. The work is published in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
“A few years ago, we discovered that cheap and transparent phosphate salt crystals, like those in soil fertilizers, can be incorporated into various parts of the sandwich-like lead halide perovskite devices, like photodetectors, LEDs or solar cells,” says Endre Horvth, the study’s first author. “These salts instantaneously react with lead ions in the presence of water, and precipitate them into extremely non-water-soluble lead phosphates.”
“The ‘fail-safe’ chemistry keeps lead ions from leaching out and can render perovskite devices safer to use in the environment or close to humans,” says Mrton Kollr, the chemist behind the growth of perovskite crystals.
“We show that this approach can be used to build functional photodetectors, and we suggest that the broad community of researchers and R&D centers working on various devices like solar cells and light-emitting diodes implements it in their respective prototypes,” adds Pavao Andričevic, who characterized the sensitive photodetectors.
Forr concludes: “This is an extremely important study – I would say, a central one – for large-scale commercialization of perovskite-based solar cells.”
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Nik Papageorgiou
@EPFL_en
Copyright © Ecole Polytechnique Fdrale de Lausanne
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
News and information
![]() Scientists create rechargeable swimming microrobots using oil and water July 16th, 2021
Scientists create rechargeable swimming microrobots using oil and water July 16th, 2021
![]() Researchers discover a new inorganic material with lowest thermal conductivity ever reported July 16th, 2021
Researchers discover a new inorganic material with lowest thermal conductivity ever reported July 16th, 2021
![]() Primers with graphene nanotubes offer a new solution for electrostatic painting of automotive parts July 16th, 2021
Primers with graphene nanotubes offer a new solution for electrostatic painting of automotive parts July 16th, 2021
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
Perovskites
![]() Researchers build structured, multi-part nanocrystals with super light-emitting properties May 28th, 2021
Researchers build structured, multi-part nanocrystals with super light-emitting properties May 28th, 2021
![]() Polarization-sensitive photodetection using 2D/3D perovskite heterostructure crystal May 4th, 2021
Polarization-sensitive photodetection using 2D/3D perovskite heterostructure crystal May 4th, 2021
![]() Polarization-sensitive photodetection using 2D/3D perovskite heterostructure crystal May 4th, 2021
Polarization-sensitive photodetection using 2D/3D perovskite heterostructure crystal May 4th, 2021
Discoveries
![]() Repairs using light signals: FAU research group develops smart microparticle that identifies defective parts in electrical appliances July 16th, 2021
Repairs using light signals: FAU research group develops smart microparticle that identifies defective parts in electrical appliances July 16th, 2021
![]() Scientists create rechargeable swimming microrobots using oil and water July 16th, 2021
Scientists create rechargeable swimming microrobots using oil and water July 16th, 2021
![]() Researchers discover a new inorganic material with lowest thermal conductivity ever reported July 16th, 2021
Researchers discover a new inorganic material with lowest thermal conductivity ever reported July 16th, 2021
Announcements
![]() Scientists create rechargeable swimming microrobots using oil and water July 16th, 2021
Scientists create rechargeable swimming microrobots using oil and water July 16th, 2021
![]() Researchers discover a new inorganic material with lowest thermal conductivity ever reported July 16th, 2021
Researchers discover a new inorganic material with lowest thermal conductivity ever reported July 16th, 2021
![]() Primers with graphene nanotubes offer a new solution for electrostatic painting of automotive parts July 16th, 2021
Primers with graphene nanotubes offer a new solution for electrostatic painting of automotive parts July 16th, 2021
Energy
![]() Researchers discover a new inorganic material with lowest thermal conductivity ever reported July 16th, 2021
Researchers discover a new inorganic material with lowest thermal conductivity ever reported July 16th, 2021
![]() Light-harvesting nanoparticle catalysts show promise in quest for renewable carbon-based fuels June 25th, 2021
Light-harvesting nanoparticle catalysts show promise in quest for renewable carbon-based fuels June 25th, 2021
![]() Changing a 2D material’s symmetry can unlock its promise: Jian Shi Research Group engineers material into promising optoelectronic June 18th, 2021
Changing a 2D material’s symmetry can unlock its promise: Jian Shi Research Group engineers material into promising optoelectronic June 18th, 2021
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() The virus trap: Hollow nano-objects made of DNA could trap viruses and render them harmless July 16th, 2021
The virus trap: Hollow nano-objects made of DNA could trap viruses and render them harmless July 16th, 2021
![]() Scientists create rechargeable swimming microrobots using oil and water July 16th, 2021
Scientists create rechargeable swimming microrobots using oil and water July 16th, 2021
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Changing a 2D material’s symmetry can unlock its promise: Jian Shi Research Group engineers material into promising optoelectronic June 18th, 2021
Changing a 2D material’s symmetry can unlock its promise: Jian Shi Research Group engineers material into promising optoelectronic June 18th, 2021
![]() Molecular coating enhances organic solar cells June 11th, 2021
Molecular coating enhances organic solar cells June 11th, 2021
![]() Researchers build structured, multi-part nanocrystals with super light-emitting properties May 28th, 2021
Researchers build structured, multi-part nanocrystals with super light-emitting properties May 28th, 2021