Home > Press > Research breakthrough could be significant for quantum computing future: Irish-based scientists confirm crucial characteristic of new superconductor material
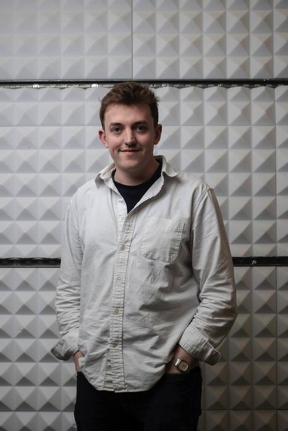 |
| Joe Carroll, a PhD researcher working with Prof. of Quantum Physics Séamus Davis at the Macroscopic Quantum Matter Group laboratory in University College Cork, lead author on a paper have discovered a spatially modulating superconducting state in a new and unusual superconductor Uranium Ditelluride (UTe2).
CREDIT Clare Keogh/UCC |
Abstract:
Scientists using one of the worlds most powerful quantum microscopes have made a discovery that could have significant consequences for the future of computing.
Research breakthrough could be significant for quantum computing future: Irish-based scientists confirm crucial characteristic of new superconductor material
Cork, Ireland | Posted on June 30th, 2023
Researchers at the Macroscopic Quantum Matter Group laboratory in University College Cork (UCC) have discovered a spatially modulating superconducting state in a new and unusual superconductor Uranium Ditelluride (UTe2). This new superconductor may provide a solution to one of quantum computings greatest challenges.
Their finding has been published in the prestigious journal Nature.
Lead author Joe Carroll, a PhD researcher working with UCC Prof. of Quantum Physics Séamus Davis, explains the subject of the paper.
Superconductors are amazing materials which have many strange and unusual properties. Most famously they allow electricity to flow with zero resistance. That is, if you pass a current through them they dont start to heat up, in fact, they dont dissipate any energy despite carrying a huge current. They can do this because instead of individual electrons moving through the metal we have pairs of electrons which bind together. These pairs of electrons together form macroscopic quantum mechanical fluid.
What our team found was that some of the electron pairs form a new crystal structure embedded in this background fluid. These types of states were first discovered by our group in 2016 and are now called Electron Pair-Density Waves. These Pair Density Waves are a new form of superconducting matter the properties of which we are still discovering.
What is particularly exciting for us and the wider community is that UTe2 appears to be a new type of superconductor. Physicists have been searching for a material like it for nearly 40 years. The pairs of electrons appear to have intrinsic angular momentum. If this is true, then what we have detected is the first Pair-Density Wave composed of these exotic pairs of electrons.
When asked about the practical implications of this work Mr. Carroll explained;
There are indications that UTe2 is a special type of superconductor that could have huge consequences for quantum computing.
Typical, classical, computers use bits to store and manipulate information. Quantum computers rely on quantum bits or qubits to do the same. The problem facing existing quantum computers is that each qubit must be in a superposition with two different energies – just as Schrödingers cat could be called both dead and alive. This quantum state is very easily destroyed by collapsing into the lowest energy state dead – thereby cutting off any useful computation.
This places huge limits on the application of quantum computers. However, since its discovery five years ago there has been a huge amount of research on UTe2 with evidence pointing to it being a superconductor which may be used as a basis for topological quantum computing. In such materials there is no limit on the lifetime of the qubit during computation opening up many new ways for more stable and useful quantum computers. In fact, Microsoft have already invested billions of dollars into topological quantum computing so this is a well-established theoretical science already. he said.
What the community has been searching for is a relevant topological superconductor; UTe2 appears to be that.
What weve discovered then provides another piece to the puzzle of UTe2. To make applications using materials like this we must understand their fundamental superconducting properties. All of modern science moves step by step. We are delighted to have contributed to the understanding of a material which could bring us closer to much more practical quantum computers.
Congratulating the research team at the Macroscopic Quantum Matter Group Laboratory in University College Cork, Professor John F. Cryan, Vice President Research and Innovation said:
This important discovery will have significant consequences for the future of quantum computing. In the coming weeks, the University will launch UCC Futures – Future Quantum and Photonics and research led by Professor Seamus Davis and the Macroscopic Quantum Matter Group, with the use of one of the world’s most powerful microscopes, will play a crucial role in this exciting initiative.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Eoin Hahessy
University College Cork
Cell: 00353860468950
Copyright © University College Cork
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
Quantum Physics
![]()
Electron collider on a chip June 30th, 2023
![]()
USTC enhances fluorescence brightness of single silicon carbide spin color centers June 9th, 2023
![]()
Single quantum bit achieves complex systems modeling June 9th, 2023
News and information
![]()
Electron collider on a chip June 30th, 2023
![]()
Discovering features of band topology in amorphous thin films June 30th, 2023
Imaging
![]()
New single-photon Raman lidar can monitor for underwater oil leaks: System could be used aboard underwater vehicles for many applications June 30th, 2023
![]()
The picture of health: Virginia Tech researchers enhance bioimaging and sensing with quantum photonics June 30th, 2023
![]()
Nanobiotechnology: How Nanomaterials Can Solve Biological and Medical Problems April 14th, 2023
Superconductivity
![]()
Researchers at Purdue discover superconductive images are actually 3D and disorder-driven fractals May 12th, 2023
Possible Futures
![]()
CityU awarded invention: Soft, ultrathin photonic material cools down wearable electronic devices June 30th, 2023
![]()
The picture of health: Virginia Tech researchers enhance bioimaging and sensing with quantum photonics June 30th, 2023
Chip Technology
![]()
Electron collider on a chip June 30th, 2023
![]()
Discovering features of band topology in amorphous thin films June 30th, 2023
![]()
Breaking through the limits of stretchable semiconductors with molecular brakes that harness light June 9th, 2023
Quantum Computing
![]()
Electron collider on a chip June 30th, 2023
![]()
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Discoveries
![]()
CityU awarded invention: Soft, ultrathin photonic material cools down wearable electronic devices June 30th, 2023
![]()
The picture of health: Virginia Tech researchers enhance bioimaging and sensing with quantum photonics June 30th, 2023
Announcements
![]()
New single-photon Raman lidar can monitor for underwater oil leaks: System could be used aboard underwater vehicles for many applications June 30th, 2023
![]()
CityU awarded invention: Soft, ultrathin photonic material cools down wearable electronic devices June 30th, 2023
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]()
New single-photon Raman lidar can monitor for underwater oil leaks: System could be used aboard underwater vehicles for many applications June 30th, 2023
![]()
CityU awarded invention: Soft, ultrathin photonic material cools down wearable electronic devices June 30th, 2023
![]()
The picture of health: Virginia Tech researchers enhance bioimaging and sensing with quantum photonics June 30th, 2023
Tools
![]()
New single-photon Raman lidar can monitor for underwater oil leaks: System could be used aboard underwater vehicles for many applications June 30th, 2023
![]()
Understanding the mechanism of non-uniform formation of diamond film on tools: Paving the way to a dry process with less environmental impact March 24th, 2023
![]()
Novel microscope developed to design better high-performance batteries: Innovation gives researchers inside view of how batteries work February 10th, 2023










