Home > Press > Solving a superconducting mystery with more precise computations: New method from Clemson University researcher, enabled by Frontera supercomputer, helps explain role of phonons in copper-based superconductivity
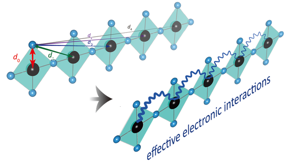 |
| A conceptual representation of the role of phonons in cuprate superconductivity.
CREDIT Yao Wang, Clemson University |
Abstract:
Researchers have known about high-temperature superconducting copper-based materials, or cuprates, since the 1980s. Below a certain temperature (approximately -130 degree Celsius), electrical resistance vanishes from these materials and magnetic flux fields are expelled. However, the basis for that superconductivity continues to be debated and explored.
Solving a superconducting mystery with more precise computations: New method from Clemson University researcher, enabled by Frontera supercomputer, helps explain role of phonons in copper-based superconductivity
Austin, TX | Posted on January 28th, 2022
“It has been widely accepted that traditional superconductors result from electrons interacting with phonons, where the phonons pair two electrons as an entity and the latter can run in a material without resistance, said Yao Wang, assistant professor of physics and astronomy at Clemson University.
However, in cuprates, strong repulsions known as the Coulomb force were found between electrons and were believed to be the cause of this special and high-temperature superconductivity.
Phonons are the vibrational energy that arise from oscillating atoms within a crystal. The behavior and dynamics of phonons are very different from those of electrons, and putting these two interacting pieces of the puzzle together has been a challenge.
In November 2021, writing in the journal Physical Review Letters, Wang, along with researchers from Stanford University, presented compelling evidence that phonons are in fact contributing to a key feature observed in cuprates, which may indicate their indispensable contribution to superconductivity.
The study innovatively accounted for the forces of both electrons and phonons together. They showed that phonons impact not only electrons in their immediate vicinity, but act on electrons several neighbors away.
An important discovery in this work is that electron-phonon coupling generates non-local attractive interactions between neighboring electrons in space, Wang said. When they used only local coupling, they calculated an attractive force an order of magnitude smaller than the experimental results. This tells us that the longer-range part is dominant and extends up to four unit cells, or neighboring electrons.
Wang, who led the computational side of the project, used the National Science Foundation (NSF)-funded Frontera supercomputer at the Texas Advanced Computing Center (TACC) the fastest academic system in the world to replicate experiments carried out at the Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource and presented in Science in Sept. 2021 in a simulation.
The results relied not only on Fronteras super-fast parallel computing capabilities, but on a new mathematical and algorithmic method that allowed for far greater accuracy than ever before.
The method, called variational non-Gaussian exact diagonalization, can perform matrix multiplications on billions of elements. Its a hybrid method, Wang explained. It treats the electron and phonon by two different approaches that can adjust with each other. This method performs well and can describe strong coupling with high precision. The method development was also supported by a grant from NSF.
The demonstration of phonon-mediated attraction has a significant impact even beyond the scope of superconductors. Practically, the results mean weve found a way to manipulate Coulomb interactions, Wang said, referring to the attraction or repulsion of particles or objects because of their electric charge.
If superconductivity comes from Coulomb forces only, we cannot easily manipulate this parameter, he said. But if part of the reason comes from the phonon, then we can do something, for instance, putting the sample on some substrate that will change the electron-phonon interaction. That gives us a direction to design a better superconductor.
This research gives new insights into the mystery of cuprate superconductivity that may lead to higher temperature superconducting materials and devices, said Daryl Hess, a program director in Division of Materials Research at NSF. They may find their way into future cell phones and quantum computers. A journey started by human creativity, clever algorithms, and Frontera.
Wang and collaborator Cheng-Chien Chen, from the University of Alabama, Birmingham, also applied this new approach and powerful TACC supercomputers to study laser-induced superconductivity. They reported these findings in Physical Review X in November 2021. And working with a team from Harvard, Wang used TACC supercomputers to study the formation of Wigner crystals in work published in Nature in June 2021.
As is the case in many fields of science, supercomputers are the only tool that can probe the quantum behavior and explain the underlying phenomena at play.
In physics, we have very beautiful frameworks to describe an electron or an atom, but when were talking about real materials with 1023 atoms, we dont know how to use these beautiful frameworks, Wang said.
For quantum or correlated materials in particular, physicists have had a hard time applying beautiful theory. So instead, we use ugly theory numerical simulation of the materials. Although we dont have a well-established quantum computer for now, using classical high performance computers, we can push the problem forward a lot. Ultimately, this will guide experiment.
Wang is currently working with IBM and IonQ to develop quantum algorithms to test on current and future quantum computers. Supercomputing is our first step.
When it comes to big future developments in technology, Wang believes computational studies, in conjunction with experiment, observation and theory, will help untangle mysteries and achieve practical goals, like tunable superconducting materials.
A new algorithm can make a difference. More numerical precision can make a difference, he said. Sometimes we dont understand the nature of a phenomenon because we didnt look closely enough at the details. Only when you push the simulation and zoom in to the nth digit will some important aspect of nature show up.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Aaron Dubrow
University of Texas at Austin, Texas Advanced Computing Center
Office: 512-471-8217
Copyright © University of Texas at Austin, Texas Advanced Computing Center
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
News and information
![]()
Scientists enhance energy storage capacity of graphene supercapacitors via solar heating January 28th, 2022
![]()
HKUST co-led study reveals topology at the corner of the dining table January 28th, 2022
Superconductivity
![]()
Resolving the puzzles of graphene superconductivity: Physicists publish a theoretical framework to explain the recent discovery of superconductivity in trilayer graphene December 10th, 2021
![]()
A new dimension in magnetism and superconductivity launched November 5th, 2021
Possible Futures
![]()
Scientists enhance energy storage capacity of graphene supercapacitors via solar heating January 28th, 2022
![]()
Void-confinement effect of nanoreactor promotes heterogeneous catalysis January 28th, 2022
Discoveries
![]()
Scientists enhance energy storage capacity of graphene supercapacitors via solar heating January 28th, 2022
![]()
Void-confinement effect of nanoreactor promotes heterogeneous catalysis January 28th, 2022
![]()
2D materials could be used to simulate brain synapses in computers January 28th, 2022
Announcements
![]()
New approach transports trapped ions to create entangling gates January 28th, 2022
![]()
Acceleration of cancer biomarker detection for point of care diagnostics January 28th, 2022
![]()
HKUST co-led study reveals topology at the corner of the dining table January 28th, 2022
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]()
New approach transports trapped ions to create entangling gates January 28th, 2022
![]()
Acceleration of cancer biomarker detection for point of care diagnostics January 28th, 2022
![]()
HKUST co-led study reveals topology at the corner of the dining table January 28th, 2022










