Home > Press > Surface microstructures of lunar soil returned by Change-5 mission reveal an intermediate stage in space weathering process
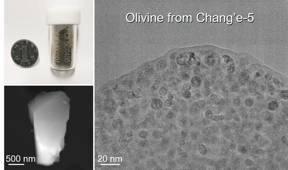 |
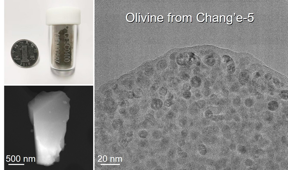
| FeO-nanoparticle-embedded amorphous rim outside of olivine grain returned by Change-5 mission
CREDIT ©Science China Press |
Abstract:
This study is conducted by a joint team from Chinese Academy of Sciences. They use aberration-corrected transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Electron-energy loss spectroscopy (EELS) and scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) to examine the microstructures and chemical compositions at nano/atomic scales of 25 soil grains (1-3 μm in size) from Sample CE5C0400YJFM00507 (1.5 g).
Surface microstructures of lunar soil returned by Change-5 mission reveal an intermediate stage in space weathering process
Beijing, China | Posted on September 30th, 2022
The soil mainly includes minerals olivine, pyroxene, anorthite and glass bead. To avoid possible chemical contamination and ion-bombing-induced amorphization, they do not employ the focused ion beam (FIB) to cut the bulk samples except glass bead. Firstly, they unambiguously identify the wüstite FeO nanoparticles instead of npFe0 that are embedded in amorphous SixOy rims outside the olivine grains. This unique rim structure has not been reported for any other lunar, terrestrial, Martian, or meteorite samples so far. Given that the nano-phase Fe is the final product of decomposing olivine Fe2SiO4, they suggest that wüstite FeO may serve as an intermediate state of the thermal decomposition process, and then the FeO may further transform into nano-phase Fe with the aid of in the presence of cosmic radiation or solar flare. Secondly, for pyroxene and anorthite, the chemical compositions of surface areas are identical to interior parts, and there is no SixOy rim outside sample. Meanwhile, no foreign volatile elements deposition layer and solar flare tracks can be found on the surface or inside the olivine and other minerals. Such findings imply that the studied samples do not undergo severe space weathering, and the underlying mechanism deserves further investigation. It provides clues or constraints on the incipient formation mechanism of rim structure under space weathering.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Bei Yan
Science China Press
Expert Contact
Jian-gang Guo
Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Copyright © Science China Press
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
News and information
![]()
Drawing data in nanometer scale September 30th, 2022
![]()
Researchers unveil mystery inside Li- o2 batteries September 30th, 2022
![]()
Synthesis of air-stable room-temperature van der Waals magnetic thin flakes September 30th, 2022
Possible Futures
![]()
Researchers unveil mystery inside Li- o2 batteries September 30th, 2022
![]()
Synthesis of air-stable room-temperature van der Waals magnetic thin flakes September 30th, 2022
![]()
Layer Hall effect and hidden Berry curvature in antiferromagnetic insulators September 30th, 2022
Discoveries
![]()
Researchers unveil mystery inside Li- o2 batteries September 30th, 2022
![]()
Synthesis of air-stable room-temperature van der Waals magnetic thin flakes September 30th, 2022
![]()
Layer Hall effect and hidden Berry curvature in antiferromagnetic insulators September 30th, 2022
Announcements
![]()
Researchers unveil mystery inside Li- o2 batteries September 30th, 2022
![]()
Synthesis of air-stable room-temperature van der Waals magnetic thin flakes September 30th, 2022
![]()
Layer Hall effect and hidden Berry curvature in antiferromagnetic insulators September 30th, 2022
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]()
Conformal optical black hole for cavity September 30th, 2022
![]()
Ultrasmall VN/Co heterostructure with optimized N active sites anchored in N-doped graphitic nanocarbons for boosting hydrogen evolution September 30th, 2022
![]()
Layer Hall effect and hidden Berry curvature in antiferromagnetic insulators September 30th, 2022
Aerospace/Space
![]()
Strain-sensing smart skin ready to deploy: Nanotube-embedded coating detects threats from wear and tear in large structures July 15th, 2022
![]()
Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
![]()
Lightening up the nanoscale long-wavelength optoelectronics May 13th, 2022