Home > Press > Switching on a superfluid: Exotic phase transitions unlock pathways to future, superfluid-based technologies
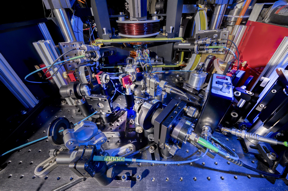 |
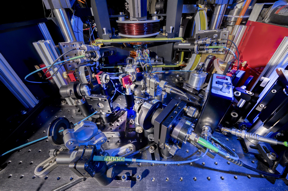
| The ultracold atomic lab at Swinburne University of Technology
CREDIT Swinburne University of Technology |
Abstract:
We can learn a lot by studying microscopic and macroscopic changes in a material as it crosses from one phase to another, for example from ice to water to steam. A new Australian study examines systems transitioning from normal fluid to a quantum state known as a superfluid, which can flow with zero friction, with a view to future, superfluid-based, quantum technologies, such as ultra-low energy electronics.We can learn a lot by studying microscopic and macroscopic changes in a material as it crosses from one phase to another, for example from ice to water to steam.
Switching on a superfluid: Exotic phase transitions unlock pathways to future, superfluid-based technologies
Melbourne, Australia | Posted on September 24th, 2021
But while these phase transitions are well understood in the case of water, much less is known about the dynamics when a system goes from being a normal fluid to a superfluid, which can flow with zero friction, ie without losing any energy.
A new Swinburne study observing transition of an atomic gas from normal fluid to superfluid provides new insights into the formation of these remarkable states, with a view to future, superfluid-based, quantum technologies, such as ultra-low energy electronics.
Superfluid formation was seen to involve a number of different timescales, associated with different dynamical processes that take place upon crossing the phase boundary.
UNDERSTANDING DYNAMIC TRANSITIONS, TOWARDS FUTURE TECHNOLOGIES
As a nonequilibrium, dynamic process, phase transitions are challenging to understand from a theoretical perspective, inside these fascinating and potentially useful states of matter.
Such non-equilibrium phenomena in many-body quantum systems involves a complex interplay of correlations spanning vastly different spatio-temporal scales. Access to the full dynamics in most materials can be prohibited by the ultrashort timescales.
Future technologies based on quantum states such as superfluids or superconductors will need to be switched (on/off), so understanding how systems evolve after switching answers important basic questions, such as how fast such devices can operate.
Forming a superfluid involves the correlated motion of the many microscopic constituents within a large collection of quantum-mechanical particles.
Dilute gases of ultracold atoms however, allow measurements of real-time dynamics on accessible timescales, explains lead author Dr Paul Dyke (Swinburne).
Here we use an ultracold gas of strongly interacting fermionic atoms (ie, a Fermi gas), to study how the correlations required to form a superfluid build up after a sudden quench of the interactions. This takes the system out of equilibrium.
By measuring the subsequent dynamics as the system returns to equilibrium we can resolve the different timescales involved, for the various correlations to build up. These timescales depend on the corresponding length scales, with short range correlations and pair formation developing quickly, while the overall momentum distribution can take several orders of magnitude longer to reach equilibrium.
The new experiment showed that:
Formation and condensation of fermion pairs can take place on very different timescales, depending on the speed of the quench.
The contact parameter is seen to respond very quickly to changes in the interaction strength, indicating that short-range correlations, evolve far more rapidly than the long-range correlations necessary to form a Bose-Einstein condensate of atom pairs.
The contact parameter quantifies the likelihood of finding two atoms in very close proximity to each other, and is strongly enhanced when atoms form pairs.
THE STUDY
Dynamics of a Fermi Gas Quenched to Unitarity was published in Physical Review Letters in September 2021 (DOi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.127.100405)
As well as thanks to the Australian Research Council for funding, the authors acknowledged colleagues Tapio Simula (Swinburne), Meera Parish and Jesper Levinsen (Monash/FLEET) and Matthew Davis (UQ/FLEET) for helpful discussions and feedback.
ULTRA-COLD GAS STUDIES AT FLEET
Researchers often use ultra-cold atoms to study quantum systems, because of the ability to perfectly tune atomic interactions.
Quantum gases of ultra-cold, neutral atoms are now helping unlock the fundamental physics of Fermi systems, often uncovering phenomena not readily accessible in other systems.
By increasing the interaction strength between fermionic atoms, experiments can explore the unitary limit, where the atomic behaviour is expected to reveal universal features of interacting fermions that could connect our understanding of superconductivity and Bose-Einstein condensation.
Fundamental discoveries made from experiments such as these can help guide FLEETs quest to develop dynamically switchable materials in which particles can move without dissipating energy, explains corresponding author Prof Chris Vale.
Chris Vale leads FLEETs studies of quantum gases at Swinburne University of Technology, where his lab routinely cools atomic gases to temperatures approaching Absolute Zero. In this temperature range, quantum behaviours that are usually only found at a microscopic level become prominent at a macroscopic level.
Chris is one of over one-hundred FLEET researchers, all motivated by one grand challenge: to reduce the energy used in information and communication technology (ICT), which already accounts for at least 8% of global electricity use, and is doubling every decade.
FLEET (the ARC Centre of Excellence in Future Low-Energy Electronics Technologies) will develop systems in which electricity flows with minimal resistance and therefore minimal wasted dissipation of energy, and devices in which this dissipationless electric current can be switched on and off at will.
These devices will enable revolutionary new electronics and communications technologies with ultra-low energy consumption.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Errol Hunt
ARC Centre of Excellence in Future Low-Energy Electronics Technologies
Office: 042-313-9210
Expert Contact
Prof Chris Vale
Swinburne University of Technology
Copyright © ARC Centre of Excellence in Future Low-Energy Electronics Technologies (FLEET)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
News and information
![]() Brought into line: FAU physicists control the flow of electron pulses through a nanostructure channel September 24th, 2021
Brought into line: FAU physicists control the flow of electron pulses through a nanostructure channel September 24th, 2021
![]() Nanocellulose decorated with proteins is suitable for 3D cell culturing September 24th, 2021
Nanocellulose decorated with proteins is suitable for 3D cell culturing September 24th, 2021
![]() Researchers use breakthrough method to answer key question about electron states September 24th, 2021
Researchers use breakthrough method to answer key question about electron states September 24th, 2021
Physics
![]() Ultrasound at the nanometre scale reveals the nature of force September 17th, 2021
Ultrasound at the nanometre scale reveals the nature of force September 17th, 2021
![]() Ultrafast & ultrathin: new physics professor at TU Dresden makes mysterious quantum world visible September 10th, 2021
Ultrafast & ultrathin: new physics professor at TU Dresden makes mysterious quantum world visible September 10th, 2021
Quantum Physics
![]() Engineering various sources of loss provides new features for perfect light absorption: “Loss is ubiquitous in nature, and by better understanding it, we make it more useful” September 10th, 2021
Engineering various sources of loss provides new features for perfect light absorption: “Loss is ubiquitous in nature, and by better understanding it, we make it more useful” September 10th, 2021
![]() Tapping into magnets to clamp down on noise in quantum information September 9th, 2021
Tapping into magnets to clamp down on noise in quantum information September 9th, 2021
![]() Putting a new theory of many-particle quantum systems to the test: Experiments show that generalized hydrodynamics accurately simulates an out-of-equilibrium quantum system September 3rd, 2021
Putting a new theory of many-particle quantum systems to the test: Experiments show that generalized hydrodynamics accurately simulates an out-of-equilibrium quantum system September 3rd, 2021
Chip Technology
![]() Micro-scale opto-thermo-mechanical actuation in the dry adhesive regime Peer-Reviewed Publication September 24th, 2021
Micro-scale opto-thermo-mechanical actuation in the dry adhesive regime Peer-Reviewed Publication September 24th, 2021
![]() Brought into line: FAU physicists control the flow of electron pulses through a nanostructure channel September 24th, 2021
Brought into line: FAU physicists control the flow of electron pulses through a nanostructure channel September 24th, 2021
Discoveries
![]() Brought into line: FAU physicists control the flow of electron pulses through a nanostructure channel September 24th, 2021
Brought into line: FAU physicists control the flow of electron pulses through a nanostructure channel September 24th, 2021
![]() Nanocellulose decorated with proteins is suitable for 3D cell culturing September 24th, 2021
Nanocellulose decorated with proteins is suitable for 3D cell culturing September 24th, 2021
![]() Researchers use breakthrough method to answer key question about electron states September 24th, 2021
Researchers use breakthrough method to answer key question about electron states September 24th, 2021
Announcements
![]() Brought into line: FAU physicists control the flow of electron pulses through a nanostructure channel September 24th, 2021
Brought into line: FAU physicists control the flow of electron pulses through a nanostructure channel September 24th, 2021
![]() Nanocellulose decorated with proteins is suitable for 3D cell culturing September 24th, 2021
Nanocellulose decorated with proteins is suitable for 3D cell culturing September 24th, 2021
![]() Researchers use breakthrough method to answer key question about electron states September 24th, 2021
Researchers use breakthrough method to answer key question about electron states September 24th, 2021
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Micro-scale opto-thermo-mechanical actuation in the dry adhesive regime Peer-Reviewed Publication September 24th, 2021
Micro-scale opto-thermo-mechanical actuation in the dry adhesive regime Peer-Reviewed Publication September 24th, 2021
![]() MXene-GaN van der Waals metal-semiconductor junctions for high performance photodetection September 24th, 2021
MXene-GaN van der Waals metal-semiconductor junctions for high performance photodetection September 24th, 2021
![]() Brought into line: FAU physicists control the flow of electron pulses through a nanostructure channel September 24th, 2021
Brought into line: FAU physicists control the flow of electron pulses through a nanostructure channel September 24th, 2021