Home > Press > Two-dimensional bipolar magnetic semiconductors with high Curie-temperature and electrically controllable spin polarization realized in exfoliated Cr(pyrazine)2 monolayers
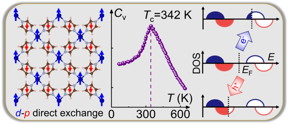 |
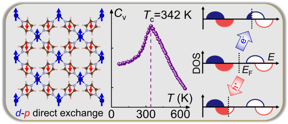
| On the left, a strong d-p direct exchange magnetic interaction exists between Cr cations and pyrazine radicals. In the center, the Curie temperature Tc is displayed. On the right shows that the Cr(pyrazine)2 monolayer is an intrinsic bipolar magnetic semiconductor where electrical doping can induce half-metallic conduction with controllable spin-polarization direction. Photo credit: Xiangyang Li and Xingxing Li.
CREDIT ©Science China Press |
Abstract:
Recently, SCIENCE CHINA Chemistry published online the important research results by Prof. Jinlong Yangs research group from University of Science and Technology of China in the field of two-dimensional magnetic semiconductors.
Two-dimensional bipolar magnetic semiconductors with high Curie-temperature and electrically controllable spin polarization realized in exfoliated Cr(pyrazine)2 monolayers
Beijing, China | Posted on December 3rd, 2021
Two dimensional (2D) magnetic semiconductors, integrating semiconductivity, ferromagnetism and low dimensionality, serve as the cornerstone for high-speed nanospintronic devices. However, the practical applications of nowadays 2D magnetic semiconductors face two key problems: the rather low magnetic Curie temperature compared to room temperature, and the lack of a simple and efficient method to control the carriers spin polarization direction. Thus, exploring 2D magnetic semiconductors with room temperature magnetic ordering and controllable spin polarization is highly desirable.
On the one hand, in order to raise the magnetic Curie temperature to room temperature, Prof. Jinlong Yangs research group has previously proposed to introduce a type of strong d-p direct ferrimagnetic exchange interaction between transition metal cations and magnetic organic linker radical anions (see below, left image) in rectangular 2D organometallic lattices such as Cr(pentalene)2 and Cr(DPP)2 [J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 109; J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 2439]. However, up to now, their experimental realization still keeps as an open question. Also, the control of spin polarization has not been achieved therein.
On the other hand, in order to realize direct control of carriers spin polarization simply by electrical gating, Prof. Jinlong Yangs research group has previously proposed a novel class of spintronic materials named bipolar magnetic semiconductors (BMS) [Nanoscale 2012, 4, 5680; Natl. Sci. Rev. 2016, 3, 365], which can provide completely spin polarized currents with the spin polarization direction reversible by altering the polarity of applied voltage gate. It is worth mentioning that the most promising 2D material with BMS function is our designed 2D MnPSe3 nanosheets, where spin-polarization directions are opposite for electron and hole doping, and can be controlled by applying an external voltage gate. [J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 11065]. However, the ground magnetic state of 2D MnPSe3 is antiferromagnetic and should be doped to become a ferromagnetic BMS. Moreover, the magnetic Curie temperature under doping is low (up to 206 K), far from practical application.
Here, by marriage of our recently proposed d-p direct ferrimagnetic exchange scheme and the concept of bipolar magnetic semiconductors (BMS), Prof. Jinlong Yangs research group has made a significant step forward and realized a 2D intrinsic BMS material with room temperature ferrimagnetic ordering and electrically controllable spin polarization by exfoliating the recently synthesized organometallic layered crystal Li0.7[Cr(pyz)2]Cl0.7·0.25(THF) (pyz = pyrazine, THF = tetrahydrofuran) [Science 2020, 370, 587]. The feasibility of exfoliation is confirmed by the rather low exfoliation energy of 0.27 J/m2, even smaller than that of graphite. In exfoliated Cr(pyz)2 monolayer, each pyrazine ring grabs one electron from the Cr atom to become a radical anion, then a strong d-p direct exchange magnetic interaction emerges between Cr cations and pyrazine radicals, resulting in room temperature ferrimagnetism with a Curie temperature of 342 K (see below, center image). Moreover, Cr(pyz)2 monolayer is revealed to be an intrinsic bipolar magnetic semiconductor where electrical doping can induce half-metallic conduction with controllable spin-polarization direction (see below, right image).
The significance of the designed bipolar magnetic semiconductor (BMS), i.e. Cr(pyz)2 monolayer sheet, is summarized as follows:
1. Raising the magnetic Curie temperature of bipolar magnetic semiconductor (BMS) to room temperature.
2. Achieving direct control of carriers spin polarization simply by electrical gating.
3. Easy preparation by mechanical exfoliation.
Such kind of organometallic ferrimagnetic semiconductors not only provide a new opportunity to achieve high-Tc 2D magnetic semiconductors, but also has great potential in the design of electrically controlled nanospintronic devices.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Bei Yan
Science China Press
Office: 86-10-64015905
Expert Contacts
Xiaojun Wu
University of Science and Technology of China
Xingxing Li
University of Science and Technology of China
Jinlong Yang
University of Science and Technology of China
Copyright © Science China Press
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
Magnetism/Magnons
![]()
Researchers realize ultra-high precision search for exotic interactions December 3rd, 2021
![]()
Quantifying spin for future spintronics: Spin-momentum locking induced anisotropic magnetoresistance in monolayer WTe2 November 5th, 2021
![]()
A new dimension in magnetism and superconductivity launched November 5th, 2021
News and information
![]()
Optimized method to detect high-dimensional entanglement December 3rd, 2021
![]()
Scientists edge closer to probe that would inspect atherosclerotic plaques by forcing molecules to sound their presence December 3rd, 2021
![]()
Review on the femtosecond laser precision micro/nano-engineering December 3rd, 2021
2 Dimensional Materials
![]()
Developing high-performance MXene electrodes for next-generation powerful battery November 19th, 2021
![]()
A new dimension in magnetism and superconductivity launched November 5th, 2021
Possible Futures
![]()
Researchers develop polyimide-mica nanocomposite film with high resistance to low earth orbit environments December 3rd, 2021
![]()
Researchers realize ultra-high precision search for exotic interactions December 3rd, 2021
![]()
Optimized method to detect high-dimensional entanglement December 3rd, 2021
![]()
Scientists edge closer to probe that would inspect atherosclerotic plaques by forcing molecules to sound their presence December 3rd, 2021
Spintronics
![]()
Quantifying spin for future spintronics: Spin-momentum locking induced anisotropic magnetoresistance in monolayer WTe2 November 5th, 2021
![]()
A new dimension in magnetism and superconductivity launched November 5th, 2021
![]()
Two-dimensional hybrid metal halide device allows control of terahertz emissions October 1st, 2021
Chip Technology
![]()
Optimized method to detect high-dimensional entanglement December 3rd, 2021
![]()
Efficient photon upconversion at an organic semiconductor interface November 19th, 2021
![]()
Visualizing temperature transport: An unexpected technique for nanoscale characterization November 19th, 2021
![]()
A new dimension in magnetism and superconductivity launched November 5th, 2021
Discoveries
![]()
Researchers develop polyimide-mica nanocomposite film with high resistance to low earth orbit environments December 3rd, 2021
![]()
Researchers realize ultra-high precision search for exotic interactions December 3rd, 2021
![]()
Optimized method to detect high-dimensional entanglement December 3rd, 2021
![]()
Scientists edge closer to probe that would inspect atherosclerotic plaques by forcing molecules to sound their presence December 3rd, 2021
Announcements
![]()
Scientists edge closer to probe that would inspect atherosclerotic plaques by forcing molecules to sound their presence December 3rd, 2021
![]()
Review on the femtosecond laser precision micro/nano-engineering December 3rd, 2021
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]()
Using green tea as reducing reagent for the preparation of nanomaterials to synthesize ammonia December 3rd, 2021
![]()
Researchers develop polyimide-mica nanocomposite film with high resistance to low earth orbit environments December 3rd, 2021
![]()
Researchers realize ultra-high precision search for exotic interactions December 3rd, 2021