Home > Press > UT Southwestern develops nanotherapeutic to ward off liver cancer
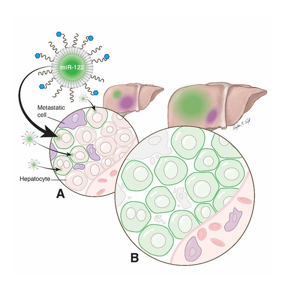 |
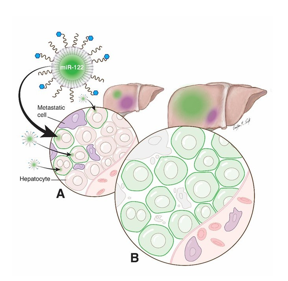
| The engineered nanoparticle encapsulates miR-122 in the core and targets hepatocytes using Gal (blue dots). it delivers the miR-122 into hepatocytes which make them healthier.
CREDIT UT Southwestern Medical Center |
Abstract:
Physician researchers from UT Southwestern Medical Center have developed an innovative nanotherapeutic drug that prevents cancer from spreading to the liver in mice.
UT Southwestern develops nanotherapeutic to ward off liver cancer
Dallas, TX | Posted on January 14th, 2022
The new liver-specific microRNA drug, developed by a team led by Andrew Wang, M.D., is a promising candidate for drug companies that developed messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccines for COVID-19, because of similarities in these RNA agents.
This might be one ray of hope that comes out of the pandemic, said Dr. Wang, Professor, Radiation Oncology, and author of a rodent-based study published in the journal Cancer Research.
It takes major funding and resources to develop nanoparticles that can deliver nucleic acids such as mRNA and miRNA. Before the development of COVID-19 vaccines, the cost was prohibitive. But now that several platforms have been developed and approved, these platforms/nanoparticles can be utilized for other applications such as what we developed in in mice models in my lab, added Dr. Wang, Radiation Oncologys Associate Vice Chair for Research, and member of the Harold C. Simmons Comprehensive Cancer Center.
The study drugs core was made by complexing miR-122 with calcium phosphate, and lipids were wrapped around the core to make the nanoparticle. The drug delivers the miR-122 into hepatocytes, which make them healthier by helping prevent cancer cells from establishing themselves in the liver. Although the drug has only been tested in mice, it is a valued advance in the fight against cancer, as up to 70 percent of people with conditions like colorectal cancer eventually develop liver metastases.
Liver metastases are second only to lung metastases, so new therapeutics in this area are an urgent need in oncology. Dr. Wangs study is promising because it showed minimal toxicity, said Carlos L. Arteaga, M.D., Director of the Harold C. Simmons Comprehensive Cancer Center, who holds The Lisa K. Simmons Distinguished Chair in Comprehensive Oncology.
Funding for the study and initial drug development was provided by National Cancer Institute/National Institutes of Health U54CA198999, NIH T32CA196589 and the University of North Carolina Research Opportunity Initiative.
####
About UT Southwestern Medical Center
UT Southwestern, one of the nations premier academic medical centers, integrates pioneering biomedical research with exceptional clinical care and education. The institutions faculty has received six Nobel Prizes, and includes 25 members of the National Academy of Sciences, 16 members of the National Academy of Medicine, and 14 Howard Hughes Medical Institute Investigators. The full-time faculty of more than 2,800 is responsible for groundbreaking medical advances and is committed to translating science-driven research quickly to new clinical treatments. UT Southwestern physicians provide care in about 80 specialties to more than 117,000 hospitalized patients, more than 360,000 emergency room cases, and oversee nearly 3 million outpatient visits a year.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
UT Southwestern Medical Center
Office: 214-648-3404
Copyright © UT Southwestern Medical Center
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
News and information
![]()
Photon recycling The key to high-efficiency perovskite solar cells January 14th, 2022
![]()
NSF funds Rice effort to measure, preserve quantum entanglement: Physicist Guido Pagano wins CAREER Award to develop tools for quantum computing January 14th, 2022
Cancer
![]()
Nanoparticle therapeutic enhances cancer immunotherapy December 17th, 2021
![]()
NYUAD study maps nanobody structure, leading to new ways to potentially fight diseases July 4th, 2021
![]()
Researchers turned transparent calcite into artificial gold June 11th, 2021
Possible Futures
![]()
The free-energy principle explains the brain January 14th, 2022
![]()
JEOL Introduces New Scanning Electron Microscope with Simple SEM Automation and Live Elemental and 3D Analysis January 14th, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]()
In vivo generation of engineered CAR T cells can repair a broken heart January 7th, 2022
Discoveries
![]()
The free-energy principle explains the brain January 14th, 2022
![]()
JEOL Introduces New Scanning Electron Microscope with Simple SEM Automation and Live Elemental and 3D Analysis January 14th, 2022
Announcements
![]()
Nanostructures get complex with electron equivalents: Nanoparticles of two different sizes break away from symmetrical designs January 14th, 2022
![]()
The free-energy principle explains the brain January 14th, 2022
![]()
JEOL Introduces New Scanning Electron Microscope with Simple SEM Automation and Live Elemental and 3D Analysis January 14th, 2022
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]()
Photon recycling The key to high-efficiency perovskite solar cells January 14th, 2022
![]()
Nanostructures get complex with electron equivalents: Nanoparticles of two different sizes break away from symmetrical designs January 14th, 2022
Nanobiotechnology
![]()
In vivo generation of engineered CAR T cells can repair a broken heart January 7th, 2022