| Mar 14, 2025 |
This novel approach significantly reduces processing time from a week to just minutes, enabling high-throughput production of precision polymer nanomaterials.
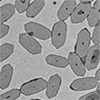
(Nanowerk News) Researchers at the University of Birmingham have developed a new method for the rapid scalable preparation of uniform nanostructures directly from block polymers.
|
|
This novel approach, led by the Dove and O’Reilly groups, significantly reduces processing time from a week to just minutes, enabling high-throughput production of precision polymer nanomaterials.
|
|
Publishing their findings in Nature Chemistry (“Direct Preparation of 2D Platelets from Polymer Enabled by Accelerated Seed Formation”), the teams outline a rapid seed preparation technique that supersaturates polymer solutions in a flow system.
|
|
The process facilitates uniform seed micelle formation and allows for the integration of seed preparation and living crystallization-driven self-assembly (CDSA). This achieves end-to-end production of nanostructures in just three minutes, surpassing existing synthetic methods by orders of magnitude.
|
|
This new method offers a powerful, scalable, and precise approach to developing diverse and complex polymer nanoparticles and paves the way for their scalable synthesis and potential applications in catalysis, biomedical engineering, and energy transfer.
|
|
Overall, the versatility and efficiency of this new method open numerous possibilities for its application in various fields and marks a significant step forward in the field of precision nanomaterials.
|
|
Dr. Rachel K. O’Reilly, one of the lead researchers, comments: “This innovative method represents a significant leap forward in the field of nanomaterials. By drastically reducing the processing time and increasing throughput, we can now produce high-quality nanostructures at a scale that was previously unattainable.”
|
|
Dr. Andrew P. Dove adds “The integration of seed preparation and living CDSA in a continuous flow setup is a game-changer. It not only enhances efficiency but also ensures uniformity and reproducibility, which are critical for the practical application of these nanostructures.”
|
|
Laihui Xiao, the first author of the study, comments, “Our flash-freezing strategy is a key innovation that allows us to achieve rapid and uniform seed formation. This breakthrough opens up new possibilities for the scalable synthesis of precision nanomaterials.”
|
|
Precision polymer nanomaterials have several potential applications including significantly advancing drug delivery systems – allowing therapeutic agents to be carried directly to targeted cells, enhancing the treatment of diseases such as cancer.
|
|
Being able to produce well-defined nanostructures quickly and efficiently also opens new possibilities in energy transfer applications – developing advanced materials for solar cells and other renewable energy technologies.
|